North America: Mature Market with Stable Demand
North America remains a dominant and mature market for power distribution automation, led primarily by the United States and Canada. The region benefits from advanced infrastructure, strong regulatory backing, and a highly competitive utility sector that prioritizes grid reliability, outage reduction, and integration of distributed energy resources (DERs). Major investments under programs such as the U.S. Department of Energy’s Grid Modernization Initiative and Canada's smart grid pilots are accelerating the deployment of SCADA systems, automated feeder switches, voltage regulators, and advanced metering infrastructure (AMI). Additionally, the proliferation of electric vehicles and rooftop solar is pushing utilities to adopt real-time automation and predictive grid control. With a strong presence of global technology providers like ABB, GE Vernova, Eaton, and Schneider Electric, North America continues to lead in innovation, pilot projects, and large-scale deployments of distribution automation systems.
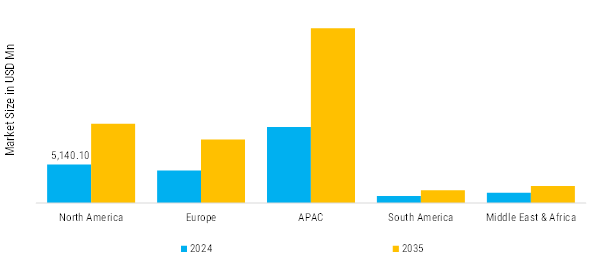
Europe: Balanced Market with Strong Regulatory Influence
Europe’s power distribution automation market is driven by stringent environmental policies, aggressive renewable energy targets, and digital infrastructure development. Countries such as Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and the Netherlands are heavily investing in grid modernization to meet the European Union’s Clean Energy for All Europeans Package and net-zero targets. The adoption of DA technologies—including SF₆-free switchgear, self-healing networks, and distributed energy resource management systems (DERMS)—has been prioritized to manage the increasing share of intermittent wind and solar power. Additionally, European utilities are at the forefront of deploying Volt-VAR optimization, real-time outage management systems, and cybersecurity solutions. The push toward smart cities, electrification of transport, and energy decentralization is further enhancing demand for automation solutions, with the region also witnessing strong public–private partnerships and cross-border innovation projects.
Asia-Pacific: Largest & Fastest-Growing Region
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing market for power distribution automation, propelled by rapid urbanization, expanding electricity access, and ambitious renewable energy goals. China leads the charge with massive state-backed smart grid rollouts, automation of substations, and deployment of real-time control technologies across urban and rural grids. India is making significant strides through programs like the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS) and Green Energy Corridor, which focus on feeder automation, substation upgrades, and advanced metering to reduce AT&C losses and enhance grid reliability. Japan, South Korea, and Australia are also advancing in grid intelligence, particularly in the context of disaster resilience, solar integration, and peak load management. The region benefits from high government spending, technological innovation, and partnerships with global and domestic automation firms, making Asia Pacific a strategic growth hotspot for DA vendors.
South America: Emerging Market with Gradual Adoption
In South America, power distribution automation adoption is steadily growing, especially in countries like Brazil, Chile, and Colombia, which are upgrading their aging grid infrastructure to improve efficiency and reduce non-technical losses. Government-backed modernization plans and international funding from organizations such as the World Bank and Inter-American Development Bank (IDB) are enabling the deployment of automated substations, smart metering, and remote monitoring systems in both urban and semi-urban areas. However, market growth is somewhat constrained by economic instability, regulatory fragmentation, and limited access to capital. Despite these challenges, rising urbanization, renewable energy installations, and a growing awareness of energy efficiency benefits are gradually encouraging utilities to adopt digital and automated solutions in their distribution networks.
Middle East & Africa: Emerging Market with High Potential
The Middle East and Africa region is emerging as a potential growth area for power distribution automation, largely driven by the need to enhance energy reliability, reduce outages, and accommodate rising energy demand in both urban and remote regions. Countries like Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates are making significant investments in smart grid and automation technologies as part of national strategies like Saudi Vision 2030 and UAE Energy Strategy 2050, which aim to increase the share of renewables and improve grid performance. In Africa, although widespread adoption remains limited due to infrastructure and financing constraints, several countries—including South Africa, Kenya, and Egypt—are piloting automation initiatives supported by development agencies and global technology partners. The combination of grid expansion, electrification programs, and utility reforms is expected to gradually build the foundation for more widespread adoption of distribution automation technologies across the MEA region.










