Market Analysis
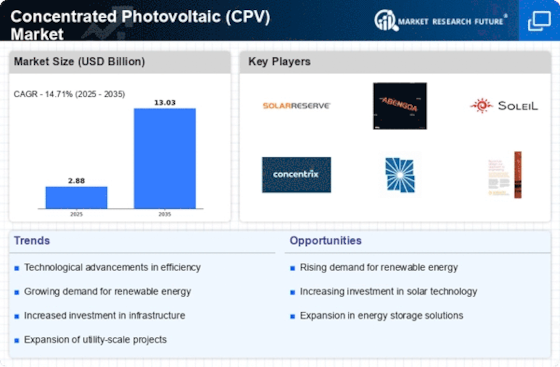
Concentrated Photovoltaic (CPV) Market (Global, 2024)
Introduction
Concentrated photovoltaics are on the way to play a major role in the transition to sustainable energy solutions. C-PV systems are increasingly gaining ground in the fight against climate change and the need for cleaner energy sources. Thanks to their small land requirement and high energy yields, they are able to generate electricity with high efficiency. The C-PV market is characterized by rapid technological progress, product innovation and a growing focus on reducing the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE). C-PV is also benefiting from the positive impact of supportive government policies and incentives aimed at promoting the use of renewable energies. The market's dynamics will be crucial to understanding the opportunities and risks in the energy transition.
PESTLE Analysis
- Political
- In 2024, government policies increasingly favoured the use of renewable energy sources. More than fifty countries had feed-in tariffs or tax credits for solar energy. For example, the United States government had allocated $US1 500 million in grants to encourage the use of photovoltaics, including CPVs. In addition, international agreements such as the Paris Agreement continued to influence national policies, and countries had committed themselves to reducing their greenhouse gas emissions by at least 40 per cent by 2030. This directly benefited the CPV market.
- Economic
- In 2024, world investment in renewable energy reached $500 billion. A significant portion of this went into the development of solar technology, including CPV systems. Since the year 2010, the price of solar energy had dropped by around 80 percent, bringing it into competition with fossil fuels. The levelized cost of electricity from a CPV system had fallen to about six cents per kilowatt-hour, which was on a par with that from traditional sources. This was why more and more governments and companies were investing in CPV.
- Social
- A survey in the United States showed that 75 per cent of the population wanted the United States to increase its investment in solar energy. In 2024, educational campaigns and community projects had raised public awareness of the advantages of concentrating solar power by 30 per cent, including its higher efficiency and lower land use requirements compared to conventional solar cells. This was reflected in a rise in the demand for CSP systems for homes and businesses.
- Technological
- The efficiency of the concentrating systems has increased, and some systems now convert more than 40 per cent of the sunlight into electricity. The introduction of new materials and designs, such as the advanced multi-junction solar cells, has reduced the cost of concentrating systems by about 15 per cent in 2024. In addition, the introduction of artificial intelligence into the tracking system has increased the energy harvest by 20 per cent, which has increased the appeal of concentrating solar power to investors and entrepreneurs.
- Legal
- In 2024 the legal framework for the use of energy from natural sources is becoming increasingly restrictive. The European Union is implementing the Renewable Energy Directive, which requires at least 32 % of energy consumption to be covered by the use of renewable energy sources by the year 2030. In order to meet these requirements, manufacturers of CPV systems must meet certain standards, the certification of which can cost up to $200,000. Nevertheless, many countries are enacting legislation to make the approval of solar projects easier, which is also promoting the growth of the CPV market.
- Environmental
- The positive impact of concentrating solar power on the environment is clearly demonstrated by the fact that for every megawatt of concentrating solar power installed, annual carbon dioxide emissions are reduced by approximately 1,000 tons. In 2024, the emphasis on environmentalism has led to a twenty-five per cent increase in the use of concentrating solar power in areas with high solar irradiation, thereby reducing our dependence on fossil fuels. The life-cycle analysis of concentrating solar power shows that it consumes fifty per cent less water than traditional solar energy, which makes it a more sustainable technology in arid regions.
Porter's Five Forces
- Threat of New Entrants
- The CPV market is characterized by a moderate degree of competition because of the significant investment required in technology and infrastructural investment. However, the barriers to entry are slowly falling, mainly because of the technological advances, but the established players with strong brands and distribution networks present a challenge to new entrants. Regulations and the need for specialist knowledge are also likely to deter new competitors.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- The bargaining power of suppliers in the CPV market is relatively low because of the wide availability of suppliers for the most important components, such as solar cells and heliostats. The easy switching between suppliers is a further damper on supplier power. Suppliers of special components might have a little more power, but overall the market is still favorable to the manufacturer.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- The buyer has high bargaining power in the CPV market, since he can choose between many suppliers and many technologies. The growing interest in green energy solutions and the availability of other solar cell technologies give the buyer an advantage in negotiations. Large buyers such as power companies can also demand lower prices and more favorable terms.
- Threat of Substitutes
- The threat of substitutes on the CPV market is moderate, as there are other solar energy technologies, such as the more traditional photovoltaics and solar thermal energy. On certain sites, CPV can be more efficient, but availability and improvements in other solar energy technology can attract customers who are looking for cost-effective solutions. However, the unique advantages of CPV in certain applications can mitigate this threat.
- Competitive Rivalry
- Competition is high in the CPV market. Many players are vying for market share. The rapid development of technology and the push for renewable energy solutions have increased competition. The companies are investing heavily in research and development to differentiate their products and improve their performance. Competition is driving innovation but also causing price wars that affect profits.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- High efficiency in converting sunlight to electricity compared to traditional PV systems.
- Ability to generate more power in smaller footprints, making it suitable for space-constrained areas.
- Technological advancements leading to reduced costs and improved performance.
Weaknesses
- Higher initial investment costs compared to conventional solar technologies.
- Dependence on direct sunlight, limiting effectiveness in cloudy or shaded environments.
- Complex installation and maintenance requirements.
Opportunities
- Growing demand for renewable energy sources and government incentives for solar energy adoption.
- Potential for integration with energy storage systems to enhance reliability.
- Expansion into emerging markets with high solar potential.
Threats
- Intense competition from traditional solar PV and other renewable energy technologies.
- Regulatory changes and potential reduction in subsidies for solar energy.
- Market volatility due to fluctuations in raw material prices.
Summary
Concentrated photovoltaics (CPV) are a unique mixture of strengths and weaknesses in the market by 2024, with high efficiency and space-saving as major advantages. However, the market is hampered by high initial costs and dependence on optimum sunlight conditions. Opportunities abound with rising demand for renewable energy and market growth, while competition and regulatory changes could threaten growth. Strategic cost reduction and diversification are key to seizing opportunities and reducing risks.

















Leave a Comment