Geopolitical Factors
Geopolitical factors are increasingly shaping the Offshore Energy Market, as nations seek to secure energy independence and reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels. Tensions in energy-rich regions often lead to volatility in oil and gas prices, prompting countries to diversify their energy portfolios. The Offshore Energy Market offers a viable alternative, with many nations investing in offshore wind and solar projects to bolster their energy security. Data suggests that countries with robust offshore energy capabilities are better positioned to withstand geopolitical shocks. Additionally, international collaborations and agreements are emerging, aimed at sharing technology and best practices in offshore energy development. This collaborative approach not only enhances the capabilities of the Offshore Energy Market but also fosters a sense of global community in addressing energy challenges.
Rising Energy Demand
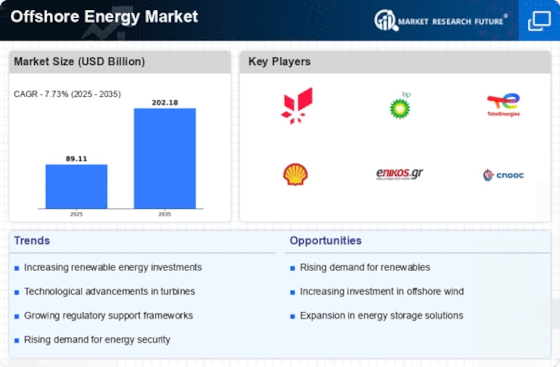
The Offshore Energy Market is experiencing a notable surge in energy demand, driven by increasing population and industrialization. As economies expand, the need for sustainable and reliable energy sources becomes paramount. According to recent data, energy consumption is projected to rise by approximately 30% by 2040. This trend compels nations to explore offshore energy solutions, particularly wind and solar, which are becoming more economically viable. The Offshore Energy Market is thus positioned to meet this demand, with investments in infrastructure and technology likely to increase significantly. Furthermore, the shift towards electrification in various sectors, including transportation and heating, further amplifies the need for offshore energy resources. This growing demand not only stimulates investment but also encourages innovation within the industry, potentially leading to more efficient energy production methods.
Investment Opportunities
Investment opportunities within the Offshore Energy Market are expanding as stakeholders recognize the potential for high returns. The increasing focus on renewable energy sources has led to a surge in capital allocation towards offshore projects. Recent reports indicate that investments in offshore wind energy alone could exceed 100 billion dollars by 2030. This influx of capital is likely to stimulate innovation and drive down costs, making offshore energy more competitive with traditional fossil fuels. Furthermore, public-private partnerships are becoming more common, allowing for shared risk and enhanced project viability. The Offshore Energy Market is thus positioned to attract a diverse range of investors, from venture capitalists to institutional funds, all seeking to capitalize on the transition to a low-carbon economy. This trend not only supports the growth of the industry but also contributes to job creation and economic development.
Environmental Regulations
The Offshore Energy Market is significantly influenced by environmental regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable practices. Governments are increasingly implementing stringent policies to combat climate change, which often include incentives for renewable energy projects. For example, many countries have set ambitious targets for carbon neutrality by mid-century, necessitating a transition to cleaner energy sources. The Offshore Energy Market stands to benefit from these regulations, as they create a favorable environment for investment in offshore wind and solar energy. Recent data suggests that investments in renewable energy are expected to reach over 2 trillion dollars by 2030, driven by regulatory frameworks. This regulatory support not only encourages the development of new projects but also enhances the credibility of the Offshore Energy Market, attracting both public and private investments.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements play a crucial role in shaping the Offshore Energy Market. Innovations in turbine design, energy storage, and grid integration are enhancing the efficiency and reliability of offshore energy projects. For instance, floating wind turbines are gaining traction, allowing for energy generation in deeper waters where traditional turbines are not feasible. The Offshore Energy Market is also witnessing improvements in predictive maintenance technologies, which can reduce operational costs and downtime. Data indicates that the levelized cost of energy for offshore wind has decreased by nearly 50% over the past decade, making it a more attractive option for investors. As technology continues to evolve, it is likely that the Offshore Energy Market will see further reductions in costs and increases in energy output, thereby attracting more stakeholders and fostering competition.