Rising Geriatric Population
The aging population is a significant demographic factor driving the Hypozincemia Drug Market. Older adults are particularly susceptible to zinc deficiency due to various factors, including decreased dietary intake and altered metabolism. As the global population ages, the prevalence of hypozincemia is expected to rise, leading to an increased demand for effective treatments. Reports indicate that the geriatric population is projected to reach 1.5 billion by 2050, which could substantially impact healthcare systems. This demographic shift necessitates a focus on addressing nutritional deficiencies, including zinc. Pharmaceutical companies are likely to respond by developing targeted therapies aimed at older adults, thereby expanding their market reach. The intersection of aging and nutritional health presents a compelling opportunity for growth within the hypozincemia drug sector.
Increasing Prevalence of Hypozincemia
The rising incidence of hypozincemia is a critical driver for the Hypozincemia Drug Market. Studies indicate that zinc deficiency affects a substantial portion of the population, particularly in developing regions. This deficiency is linked to various health issues, including impaired immune function and delayed wound healing. As awareness of these health implications grows, the demand for effective treatments is likely to increase. Furthermore, the World Health Organization has reported that zinc deficiency is a significant public health concern, which may further stimulate market growth. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, which often correlates with nutritional deficiencies, also contributes to the rising need for hypozincemia drugs. Consequently, pharmaceutical companies are focusing on developing innovative solutions to address this growing health challenge.
Advancements in Pharmaceutical Research
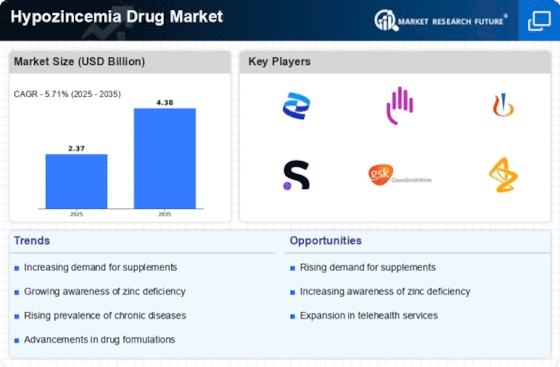
Innovations in pharmaceutical research are propelling the Hypozincemia Drug Market forward. Recent advancements in drug formulation and delivery systems have led to the development of more effective and targeted therapies for zinc deficiency. For instance, the introduction of novel zinc supplements and chelated forms of zinc has improved bioavailability, enhancing therapeutic outcomes. Additionally, research into the role of zinc in various biological processes has opened new avenues for drug development. The market is witnessing a surge in clinical trials aimed at evaluating the efficacy of these new formulations. According to industry reports, the hypozincemia drug segment is expected to experience a compound annual growth rate of over 5% in the coming years, driven by these advancements. This trend indicates a robust pipeline of innovative products that could reshape the treatment landscape for hypozincemia.
Growing Focus on Nutritional Supplements
The increasing emphasis on nutritional supplements is significantly influencing the Hypozincemia Drug Market. As consumers become more health-conscious, there is a notable shift towards preventive healthcare measures, including the use of dietary supplements. Zinc, being an essential trace element, is gaining attention for its role in maintaining overall health and preventing deficiencies. Market data suggests that the dietary supplement sector is expanding rapidly, with zinc supplements witnessing a surge in demand. This trend is further supported by endorsements from health professionals advocating for the inclusion of zinc in daily diets. Consequently, pharmaceutical companies are likely to capitalize on this trend by developing hypozincemia drugs that cater to the growing consumer base seeking nutritional solutions. The intersection of dietary supplements and pharmaceutical interventions may create new opportunities for market players.
Increased Research Funding and Initiatives
The surge in research funding and initiatives aimed at addressing nutritional deficiencies is a pivotal driver for the Hypozincemia Drug Market. Governments and health organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of zinc in public health, leading to enhanced funding for research projects focused on hypozincemia. This financial support is facilitating the exploration of new therapeutic options and the development of guidelines for zinc supplementation. Furthermore, collaborative efforts between academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies are fostering innovation in drug development. The National Institutes of Health and other organizations have allocated resources to study the implications of zinc deficiency on health outcomes, which may result in new treatment protocols. As research progresses, the insights gained are likely to translate into marketable products, thereby stimulating growth in the hypozincemia drug sector.