Dual-Use Satellites to Reshape Defense Tech Landscape in 2025
In 2025, both government offices and private innovators are likely to intensify their collaboration in tapping space assets for shared civilian and military tasks, and this coordinated effort is expected to propel dual-use satellites into a game-changing segment of the defense technology arena.
The global defense technology sector experienced a notable increase in spending, new regulations, and private innovation in 2025, driven by growing space commercial activity and complex geopolitics. That same year, the European Space Agency proposed a 1-billion-euro dual-use satellite network featuring optical and radar sensors, onboard artificial intelligence, and edge-computing modules.
The agency's initial explicit foray into dual-use assets is the initiative, which is designed to enhance both scientific monitoring and military surveillance. It is a component of a more comprehensive €6 billion space security strategy that will extend until 2035, thereby bolstering the increasing significance of dual-use satellites in the development of European defense technology in 2025.
In 2025, the American defense agenda will still focus primarily on detecting missiles in orbit. Tensions between Elon Musk and former President Donald Trump have left SpaceXs role in the planned Golden Dome shield uncertain, pushing the Pentagon to seek new commercial partners. The shift highlights how both valuable and vulnerable private companies are now in a military system built almost entirely on dual-use satellites. For NOVI Space, which is assembling a forty-satellite constellation for both military and civilian customers, the year will be a crucial test of whether its ambitious plan can attract paying users.
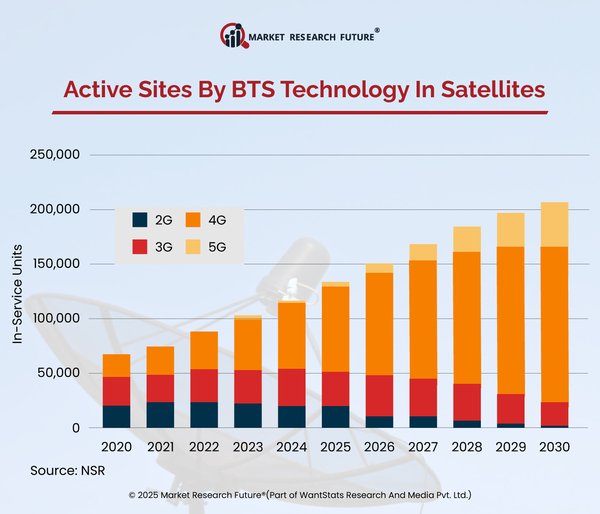
In 2023, worldwide spending on military and dual-use space systems surpassed USD 58 billion. Analysts project that outlays will grow again by 2025, propelled by public-private partnerships and venture-funded innovation. As countries seek strategic independence, dual-use satellites will stay central to defense plans, providing resilient intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) support.