Market Analysis
Cyber Insurance Market (Global, 2024)
Introduction
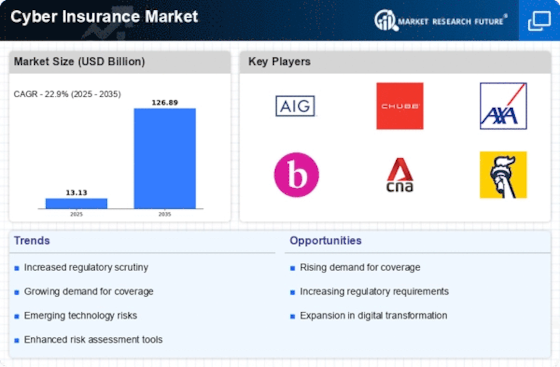
The cyber insurance market has developed as a major risk management tool for businesses in the increasingly complex cyberspace. The increasing dependence of companies on digital assets has increased the likelihood of cyber incidents such as data breaches, ransomware attacks and system failures, and has also increased the awareness of the need for robust insurance solutions. The cyber insurance market is characterised by a wide range of products and services tailored to the unique needs of different sectors, from small businesses to large corporations. The insurance industry has been adapting its products to the changing nature of the risks, using advanced analytic and risk assessment tools to understand and manage potential risks. In addition, the changing regulatory environment and the increasing focus on data protection are increasing the demand for comprehensive insurance cover, making it important for all market players to be aware of the market developments and trends. As the cyber environment evolves, the cyber insurance market is ideally positioned to protect businesses against the financial impact of cyber incidents.
PESTLE Analysis
- Political
- In 2024, the political background to the cyber insurance market is dominated by government regulations intended to improve cyber security. In the United States, the budget for cyber security includes $2.5 billion for public-private cyber security initiatives. In the European Union, the digital operational resilience act has been introduced, which requires financial institutions to have adequate cyber insurance cover. This is expected to affect some 8,000 firms across the EU. These political actions drive demand for cyber insurance, as companies strive to comply with the new regulations.
- Economic
- The economic environment for the cyber insurance market in 2024 is characterized by an increase in the costs of cyber incidents. Recent studies have indicated that the average cost of a data breach has reached $ 4,450,000, and companies are looking for insurance solutions to mitigate financial risks. Furthermore, the world's cybersecurity spending is expected to exceed $ 200 billion in 2024, indicating an increase in investments in security measures, of which cyber insurance is an important component. The economic pressures will push companies to consider cyber insurance as an essential expense.
- Social
- In 2024 the public consciousness of the dangers of cyberspace had risen considerably. In 2024, a full seventy per cent of consumers were worried about the security of their personal data. It was this increased awareness that was influencing companies to take out cyber-liability insurance, not just to protect their own assets but also to increase their customers’ trust. In addition, sixty per cent of companies had introduced training courses in cyber-security, indicating a shift in the way they thought about cyber-security. Thus the demand for cyber-liability insurance was expected to rise as companies realized the importance of protecting their reputation.
- Technological
- IT has been a long time since the market for cyber insurance began to develop. At present, a great many companies are using artificial intelligence and machine learning to assess risks and underwrite policies. By 2024, it is expected that the accuracy of risk assessment will be increased, enabling the market to offer more bespoke cover. The growth in the number of IoT devices, which is expected to reach 30 billion, will create new opportunities and challenges for cyber insurance. These devices are often the target of cyber attacks, which will increase the demand for comprehensive cover.
- Legal
- The legal framework regulating the cyber insurance market is becoming increasingly complex. In particular, new regulations have been introduced in the field of data protection and notification requirements. In 2024, the Californian Data Protection Act will be tightened with fines of up to $7,500 per infringement. This regulatory environment is pushing companies to take out cyber insurance against the risks of liability for data breaches and to ensure compliance with evolving legislation. This makes the legal environment the main driver of cyber insurance policies.
- Environmental
- Cyber insurance may not be an obvious green business, but the growing dependence on digital technology has an effect on the environment. Data centres are estimated to consume around 2% of the world’s electricity by 2024, which has led to concerns about their carbon footprint. In their efforts to reduce their impact on the environment, companies are increasingly turning to cyber insurance companies that are committed to a sustainable future. This is driving the development of new green practices, such as using renewable energy sources, which could have a positive impact on underwriting and policy offerings.
Porter's Five Forces
- Threat of New Entrants
- The cyber insurance market in 2024 faces a moderate threat of new entrants. Moderately large— a combination of increased regulatory requirements and a need for specialized knowledge in underwriting and risk assessment—the market will continue to grow, even as the demand for cyber insurance rises with the increasing number of cyber attacks. But the reputation and trust that the established players have built up may make it difficult for newcomers to enter the market. Nonetheless, technological advancements and the rise of insurtech companies may lower the barriers to entry, allowing new competitors to enter the market.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- The bargaining power of the suppliers in the cyber insurance market is relatively low. The main suppliers are data suppliers, security companies and technology vendors. The number of suppliers is large, and it is easy for the insurance companies to switch to other suppliers for the same data and services. The emergence of more and more security solutions and big data analysis tools also reduces the bargaining power of suppliers. The insurance companies can use multiple resources to improve their own services.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- In 2024, the buyers of cyber insurance will have significant negotiating power. They will be looking for comprehensive coverage and the competition among insurers will be fierce. The buyers will have the ability to compare the coverage limits and premiums, and will be able to negotiate better terms. Larger companies with substantial data assets will be in a better position to demand tailor-made solutions, which will further increase their bargaining power.
- Threat of Substitutes
- The threat of substitutes in the cyber insurance market is moderate. In other words, while traditional insurance products may not directly compete with cyber insurance, enterprises can consider alternative risk management strategies such as strengthening their own cyber defenses and self-insuring. However, the unique nature of cyber insurance, which is to provide financial protection for a particular risk, makes it difficult for substitutes to fully meet the needs of dedicated coverage.
- Competitive Rivalry
- Competition in the cyber insurance market is intense in 2024. With the frequency and severity of cyber attacks increasing, the demand for cyber insurance is also increasing, bringing many players to the market. New entrants and insurtechs compete with traditional insurance companies, and the market share is in a state of flux. The competition is so intense that companies are constantly innovating their products and prices to stand out from the competition and win customers.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Growing awareness of cyber threats among businesses and individuals.
- Increased regulatory requirements driving demand for cyber insurance.
- Diverse product offerings catering to various industries and risk profiles.
Weaknesses
- Limited understanding of policy terms and coverage among potential clients.
- High variability in premium costs based on risk assessment.
- Challenges in accurately assessing and quantifying cyber risks.
Opportunities
- Expansion into emerging markets with increasing digitalization.
- Development of tailored insurance products for specific sectors.
- Partnerships with cybersecurity firms to enhance risk management services.
Threats
- Rapidly evolving cyber threats outpacing insurance coverage.
- Increased competition leading to price wars and reduced profitability.
- Potential for regulatory changes that could impact policy structures.
Summary
The cyber insurance market in 2024 will be characterized by strong demand, driven by growing awareness of cyber risks and regulatory requirements. However, challenges such as lack of understanding of coverage and the volatility of premiums will hinder growth. Opportunities lie in expanding into new markets and developing specialized products, while threats such as the evolution of cyber threats and increased competition will threaten profit. Strategic alliances and improved risk assessment methodologies will be critical to success in this highly dynamic market.

















Leave a Comment