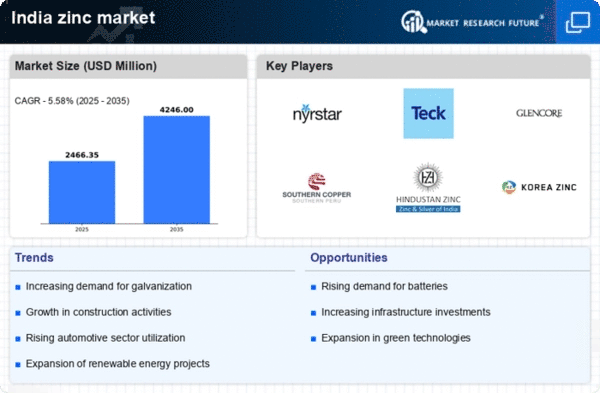
The zinc market in India is characterized by a competitive landscape that is increasingly shaped by strategic initiatives from key players. Major companies such as Hindustan Zinc Limited (IN), Glencore (CH), and Teck Resources (CA) are actively pursuing growth through various means, including technological innovation and regional expansion. Hindustan Zinc Limited, for instance, focuses on enhancing its production capabilities while also investing in sustainable practices, which positions it favorably in a market that is progressively leaning towards environmentally responsible operations. Glencore, on the other hand, appears to be concentrating on optimizing its supply chain and leveraging its global network to enhance operational efficiency, thereby influencing the competitive dynamics within the sector.The business tactics employed by these companies reflect a moderately fragmented market structure, where localized manufacturing and supply chain optimization are pivotal. The collective influence of these key players suggests a competitive environment that is not only driven by production capacity but also by the ability to adapt to changing market demands and regulatory frameworks. This adaptability is crucial as companies navigate the complexities of sourcing raw materials and meeting the evolving expectations of stakeholders.
In October Hindustan Zinc Limited (IN) announced a significant investment in a new smelting facility aimed at increasing its production capacity by 15%. This strategic move is expected to bolster its market position and enhance its ability to meet the growing demand for zinc in various sectors, including construction and automotive. The investment underscores the company's commitment to maintaining its leadership in the Indian zinc market while also addressing sustainability concerns through advanced technologies.
In September Glencore (CH) revealed plans to expand its recycling operations in India, focusing on the recovery of zinc from end-of-life products. This initiative not only aligns with global sustainability trends but also positions Glencore as a leader in the circular economy within the zinc sector. By enhancing its recycling capabilities, Glencore is likely to reduce its reliance on primary zinc production, thereby mitigating environmental impacts and responding to increasing regulatory pressures.
In August Teck Resources (CA) entered into a strategic partnership with a local Indian firm to explore new mining opportunities in the region. This collaboration is indicative of Teck's strategy to leverage local expertise and resources, which may facilitate smoother operations and enhance its competitive edge. The partnership could potentially lead to increased production efficiencies and a stronger foothold in the Indian market, reflecting a broader trend of international companies seeking local alliances to navigate complex regulatory landscapes.
As of November the competitive trends in the zinc market are increasingly defined by digitalization, sustainability, and the integration of advanced technologies such as AI. Strategic alliances are becoming more prevalent, as companies recognize the need to collaborate in order to innovate and enhance supply chain reliability. The shift from price-based competition to a focus on technological advancement and sustainable practices is likely to redefine competitive differentiation in the coming years, suggesting that companies that prioritize innovation and adaptability will be better positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape.