Growing Healthcare Expenditure
The rise in healthcare expenditure across various regions serves as a critical driver for the Dyspepsia Market. As individuals allocate more resources towards healthcare, there is a corresponding increase in spending on medications and treatments for dyspepsia. Reports suggest that healthcare spending has risen by an average of 4% annually, leading to greater accessibility of dyspepsia treatments. This trend is particularly evident in developed nations, where patients are more likely to seek medical advice and treatment for gastrointestinal issues. Consequently, the Dyspepsia Market is expected to benefit from this increased financial commitment to health, as more patients pursue effective management strategies for their dyspeptic symptoms.
Rising Prevalence of Dyspepsia
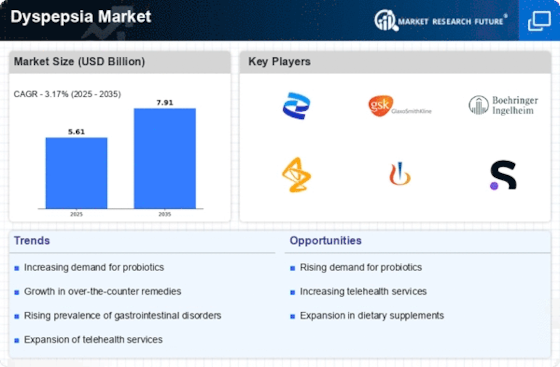
The increasing prevalence of dyspepsia is a notable driver in the Dyspepsia Market. Studies indicate that approximately 25% of the population experiences dyspeptic symptoms at some point in their lives. This rising incidence is attributed to lifestyle factors such as poor dietary habits, increased consumption of processed foods, and high-stress levels. As more individuals seek relief from these symptoms, the demand for dyspepsia treatments is likely to escalate. Consequently, pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers are focusing on developing innovative therapies and medications to address this growing concern. The Dyspepsia Market is thus poised for expansion as awareness of dyspepsia increases and more patients seek effective solutions.
Advancements in Treatment Options
Advancements in treatment options for dyspepsia significantly influence the Dyspepsia Market. Recent developments in pharmacological therapies, including proton pump inhibitors and H2-receptor antagonists, have improved symptom management for patients. Moreover, the introduction of novel therapies, such as probiotics and herbal supplements, has diversified treatment modalities available to consumers. According to market data, the global dyspepsia treatment segment is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.2% over the next five years. This growth is indicative of the increasing investment in research and development by pharmaceutical companies, aiming to enhance patient outcomes and satisfaction. As treatment options expand, the Dyspepsia Market is likely to witness a surge in demand.
Increased Focus on Preventive Healthcare
The growing emphasis on preventive healthcare is reshaping the Dyspepsia Market. As consumers become more health-conscious, there is a shift towards preventive measures that can mitigate the onset of dyspepsia. This trend is reflected in the rising popularity of dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and regular health screenings. Furthermore, healthcare providers are increasingly advocating for preventive strategies, which may include education on the importance of gut health. This proactive approach not only helps in reducing the incidence of dyspepsia but also encourages individuals to seek early treatment when symptoms arise. As a result, the Dyspepsia Market is likely to experience a shift in consumer behavior, with a growing number of patients prioritizing prevention.
Technological Innovations in Healthcare Delivery
Technological innovations in healthcare delivery are transforming the Dyspepsia Market. The integration of telemedicine and digital health platforms has made it easier for patients to access care and receive timely diagnoses. This shift is particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing dyspeptic symptoms, as they can consult healthcare professionals without the need for in-person visits. Data indicates that telehealth usage has surged, with a significant percentage of patients opting for virtual consultations. This trend not only enhances patient convenience but also encourages more individuals to seek help for their dyspepsia symptoms. As technology continues to evolve, the Dyspepsia Market is likely to adapt, leading to improved patient engagement and treatment outcomes.