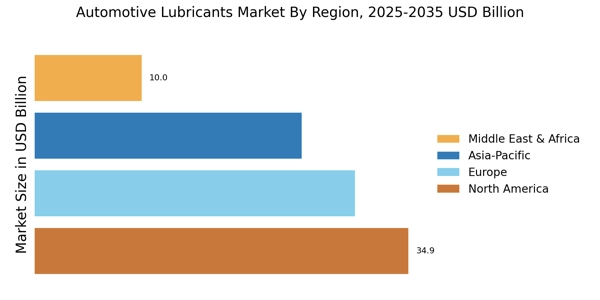
North America: Mature Market with Stable Automotive Demand
North America is considered an old yet functional market for automotive lubricants which is mainly boosted by the presence of a large fleet consisting of passenger cars, light commercial vehicles, and heavy-duty trucks. The region's demand is solely supported by the strict environmental regulations like the EPA standards which not only restrict but also promote the use of high-quality, low-emission, and fuel-efficient lubricants. Synthetic and semi-synthetic engine oils, high-performance gear oils, greases, and specialty fluids have become very common. The presence of major original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), good disposal income levels, and robust aftermarket infrastructure are other factors that contribute to the unending consumption of lubricants. Moreover, the growing attention to vehicle maintenance, longer oil change intervals, and the acceptance of hybrid/electric vehicles are steadily influencing the market for specialized and eco-friendly lubricants in the area.
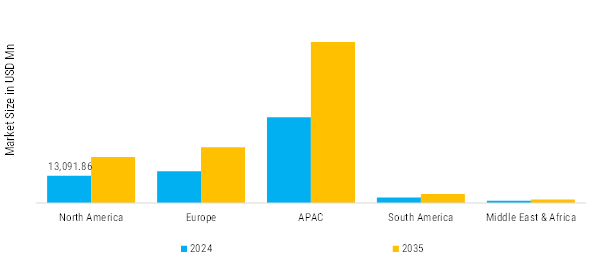
Europe: Balanced Market Driven by Stringent Emission & Performance Regulations
The premium and high-tech automotive lubricants have been setting the trends in Europe mainly due to the high regulatory requirements such as the Euro 6/7 emission controls and policies that are aimed at improving fuel economy. The demand stems from the use of lubricants in passenger cars, light commercial vehicles, heavy commercial vehicles, and the expanding electric vehicle fleet, which all need lubricants with excellent thermal stability, low viscosity, and extended service life. The market is mainly occupied by synthetic and semi-synthetic oils, while the bio-based and eco-friendly lubricants are slowly but steadily winning over the market. The well-established aftermarket channels, high acceptance of OEM-recommended products, and advanced automotive manufacturing in Europe are the factors that together promote continuous innovation and high-quality lubricant formulations.
Asia-Pacific: Largest & Fastest-Growing Region
The Asia-Pacific region has become the largest automotive lubricants market, and it is primarily due to the rapid increase in the vehicle population, urbanization in the area, and the rise in people's income. Demand for passenger cars, two-wheelers, light commercial vehicles, and heavy trucks is very large and it leads to the consumption of lubricants through Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and the aftermarket. The use of semi-synthetic and synthetic oils is increasing in the region, with India, China, and Southeast Asia being the main contributors. There, engine maintenance and fuel economy awareness are the main factors influencing lubricant selection. The growth of the logistics and e-commerce sectors has also contributed to the demand for commercial vehicle lubricants. Moreover, government programs that support electric mobility and eco-friendliness are facilitating the creation of bio-based and electric vehicle-specific lubricants in the region.
South America: Developing Market Supported by Expanding Vehicle Fleet
South America is an automotive lubricants market on the rise, with the main factors for growth being the increase in vehicle ownership, the modernization of transport fleets and, last but not least, the rising demand for maintenance services. The most significant part of the lubricant consumption goes to passenger cars, LCVs, and HCVs, which consume a variety of mineral, semi-synthetic, and synthetic products. The market is subject to the impact of the economy, government measures, and the regional trade regulations that determine the sales of both OEM and aftermarket. The increasing knowledge of engine performance, fuel efficiency, and vehicle durability is slowly changing the demand from lower-quality products to higher-quality synthetic and semi-synthetic lubricants.
Middle East & Africa: Emerging Market with Gradual Industrial & Automotive Growth
The MEA (Middle East & Africa) market is influenced by a mix of extreme weather, an increase in vehicle numbers, and the building of new infrastructure. There is a huge demand in the area for not only passenger cars but also LCVs (light commercial vehicles), HCVs (heavy commercial vehicles), and off-highway vehicles that all want lubricants to be able to stand the test of extreme heat, dust, and heavy use. In the case of high-performance and luxury vehicles, synthetic and semi-synthetic oils are being more and more used, whereas, in commercial and industrial applications, mineral oils are still very much prevalent. The market growth is bolstered by urbanization, fleet expansions, and the adoption of the latest automotive technologies, but on the other hand, economic instability and dependence on imports can alter the market situation.