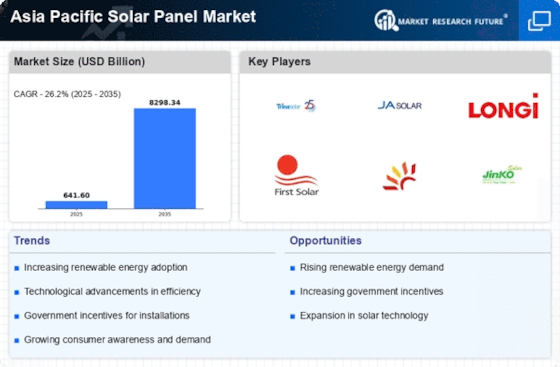
China : Unmatched Growth and Innovation
China holds a commanding 30.0% share of the APAC solar panel market, driven by robust domestic demand and government support. Key growth drivers include significant investments in renewable energy infrastructure, favorable regulatory policies, and a strong manufacturing base. The Chinese government has implemented initiatives like the Renewable Energy Law, promoting solar energy adoption and reducing tariffs on solar imports. This has led to increased consumption patterns, particularly in urban areas where energy needs are rising rapidly.
India : Government Initiatives Fuel Growth
India's solar panel market accounts for 15.0% of the APAC total, reflecting a surge in demand driven by government initiatives like the National Solar Mission. The country aims to achieve 100 GW of solar capacity by 2022, fostering a favorable investment climate. Urban centers like Delhi and Mumbai are witnessing increased solar installations, supported by incentives and subsidies. The growing middle class and rising energy costs are also propelling consumption patterns towards solar solutions.
Japan : Sustainability Meets Advanced Solutions
Japan holds an 8.0% share in the APAC solar market, characterized by a strong focus on innovative solar technologies. The government has set ambitious targets for renewable energy, particularly post-Fukushima, leading to increased investments in solar infrastructure. Demand is driven by urban areas like Tokyo and Osaka, where space constraints encourage rooftop solar installations. The competitive landscape features major players like Panasonic and Sharp, focusing on high-efficiency solar panels and energy storage solutions.
South Korea : Strong Market with Global Players
South Korea's solar panel market represents 5.0% of the APAC region, bolstered by government policies promoting renewable energy. The country has set a target of 20% renewable energy by 2030, driving demand for solar solutions. Key markets include Seoul and Busan, where urban development supports solar adoption. Major players like Hanwha Q CELLS dominate the landscape, focusing on high-efficiency products. The local market is characterized by a strong emphasis on R&D and technological advancements.
Malaysia : Government Support and Investment
Malaysia's solar panel market accounts for 3.5% of the APAC total, with significant growth potential driven by government initiatives like the Feed-in Tariff (FiT) program. This policy encourages investments in solar energy, particularly in states like Selangor and Penang. The demand for solar solutions is rising among commercial and residential sectors, supported by decreasing installation costs. Local players are increasingly collaborating with international firms to enhance technology and market reach.
Thailand : Growing Demand for Solar Solutions
Thailand's solar panel market holds a 2.5% share in APAC, driven by the government's commitment to renewable energy. The Power Development Plan aims for 30% renewable energy by 2036, fostering a favorable environment for solar investments. Key markets include Bangkok and Chiang Mai, where urbanization drives energy needs. The competitive landscape features local firms and international players, focusing on utility-scale solar projects and rooftop installations, enhancing the overall market dynamics.
Indonesia : Untapped Potential and Opportunities
Indonesia's solar panel market represents 1.5% of the APAC total, with significant untapped potential. The government is promoting renewable energy through policies like the 2025 Renewable Energy Target, aiming for 23% of energy from renewables. Key markets include Jakarta and Bali, where energy demand is increasing. The competitive landscape is evolving, with local and international players entering the market, focusing on off-grid solar solutions to address energy access challenges in rural areas.
Rest of APAC : Varied Growth Across Sub-regions
The Rest of APAC accounts for 1.16% of the solar panel market, showcasing diverse growth patterns across various countries. Regulatory frameworks and market dynamics vary significantly, influencing solar adoption rates. Countries like Vietnam and the Philippines are emerging markets, driven by government incentives and increasing energy demands. The competitive landscape includes both local and international players, focusing on tailored solutions to meet specific regional needs and challenges.