Advancements in Bioinformatics
The evolution of bioinformatics tools and software is playing a crucial role in the whole exome-sequencing market. Enhanced data analysis capabilities allow for more accurate interpretation of genetic information, which is essential for clinical applications. In Spain, the integration of advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques is expected to streamline the workflow of genetic testing laboratories. This technological progress not only improves the efficiency of whole exome sequencing but also reduces costs associated with data processing. As a result, the market is likely to witness an increase in the number of laboratories adopting these technologies, thereby expanding the overall capacity and accessibility of whole exome sequencing services.
Increased Focus on Rare Diseases
The rising prevalence of rare diseases in Spain is prompting healthcare providers to seek advanced diagnostic tools, including whole exome sequencing. As the healthcare system emphasizes the importance of identifying and treating rare genetic disorders, the whole exome-sequencing market is expected to benefit significantly. In 2025, it is estimated that around 7% of the Spanish population is affected by rare diseases, creating a substantial demand for precise genetic testing. This trend is likely to encourage healthcare professionals to adopt whole exome sequencing as a standard practice for diagnosing rare conditions, thereby driving market growth. Furthermore, patient advocacy groups are increasingly pushing for better access to genetic testing, which may further stimulate the whole exome-sequencing market.
Rising Demand for Genetic Testing
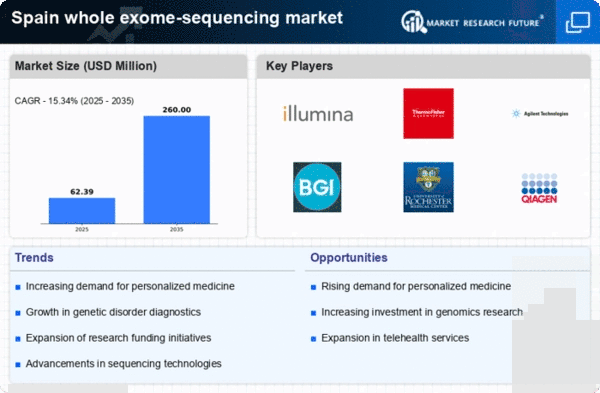
The increasing awareness of genetic disorders and the benefits of early diagnosis is driving the demand for genetic testing in Spain. As healthcare providers and patients recognize the value of personalized medicine, the whole exome-sequencing market is experiencing significant growth. In 2025, the market is projected to reach approximately €200 million, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 15% over the next five years. This trend is further supported by the Spanish government's initiatives to promote genetic research and testing, which are likely to enhance the accessibility of whole exome sequencing for various populations. As a result, the whole exome-sequencing market is poised to expand, catering to the needs of both healthcare professionals and patients seeking tailored treatment options.
Growing Investment in Genomic Research
Investment in genomic research is on the rise in Spain, driven by both public and private sectors. This influx of funding is expected to bolster the whole exome-sequencing market, as it facilitates the development of new technologies and methodologies. In recent years, Spain has seen a surge in research initiatives aimed at understanding genetic diseases, which in turn fuels the demand for whole exome sequencing. The Spanish government has allocated substantial resources to support genomic research, with funding exceeding €50 million in 2025. This financial backing is likely to enhance collaboration between academic institutions and industry players, fostering innovation and expanding the applications of whole exome sequencing in clinical settings.
Collaboration Between Healthcare and Technology Sectors
The collaboration between healthcare providers and technology companies is fostering innovation in the whole exome-sequencing market. In Spain, partnerships are emerging that aim to enhance the capabilities of genetic testing through the integration of cutting-edge technologies. These collaborations are likely to lead to the development of more efficient sequencing platforms and improved data management systems. As a result, the whole exome-sequencing market may experience accelerated growth, with new products and services entering the market. The synergy between healthcare and technology sectors is expected to create a more robust ecosystem for genetic testing, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.