Market Trends
Introduction
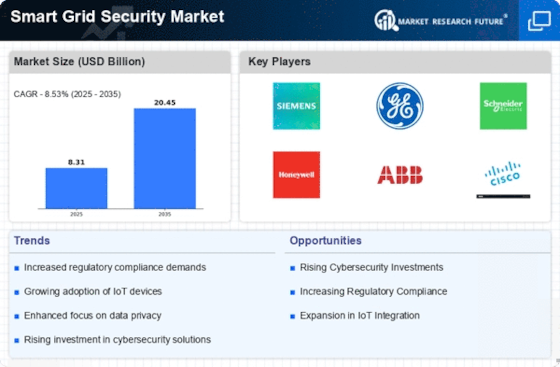
During 2023, the Smart Grid Security market is experiencing a significant transformation, resulting from a combination of technological developments, regulatory changes and changing customer behavior. Internet of Things (IoT) and the integration of renewable energy sources have accentuated the need for robust security measures to protect critical energy assets from cyber-attacks. The stricter regulatory framework is forcing the energy industry to adopt a comprehensive security framework. Also, as consumers become increasingly aware of the importance of privacy and security, they are demanding more secure energy solutions. These trends are of strategic importance for the market players, who have to find the right balance between security, operational efficiency and compliance.
Top Trends
-
Increased Cybersecurity Regulations
Governments are enacting stricter regulations for the protection of critical infrastructures, and the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has issued new guidelines. In this regard, there has been an increase in compliance-related investment, as companies are required to enhance their security frameworks. For example, the Energy Sector Cybersecurity Framework requires regular audits, which have a significant impact on operating budgets. And in the future, the penalties for noncompliance are likely to increase, further increasing the need for security solutions. -
Adoption of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are becoming a popular way of protecting the smart grid. Companies like IBM use them to detect and counteract threats. Reports say that with AI, response times can be reduced by up to 50 percent. This trend improves the detection of threats and allows for more preventive measures than merely reactionary ones. As the technology continues to evolve, the scope of automation in security will increase, resulting in the possible reorganization of operational strategies. -
Rise of IoT Security Solutions
The increasing number of IoT devices in smart grids is increasing the demand for specialized IoT security solutions. Industry leaders are working on robust security solutions to protect these devices from security breaches. A recent study found that over 70 percent of IoT devices lack proper security. As a result, industry leaders are investing heavily in IoT security frameworks. These solutions could eventually include a standardized security protocol for IoT devices that enhances the overall security of smart grids. -
Focus on Data Privacy
Smart grids collect vast amounts of data on consumers. The question of privacy is becoming ever more pressing. To protect the information on consumers, companies are introducing new encryption and anonymization techniques. A survey has shown that 80% of consumers are concerned about data privacy in smart grids. This has prompted companies to put security and transparency at the top of their priority list. In the future, companies will probably have to comply with stricter data protection regulations. -
Collaboration Between Public and Private Sectors
Hence, the trend is to have a closer cooperation between the private and public sectors. Such an alliance as the Smart Electric Power Alliance (SEPA) is bringing together partners to share their knowledge and resources. Such cooperation is essential, since 60 per cent of cyber-attacks are directed at critical infrastructure. Such a closer cooperation will in the future also lead to a common investment in security innovations, thereby making the grid more resilient. -
Investment in Incident Response Planning
Incident response planning is gaining ground as organizations prepare for the threat of cyber attacks. A study shows that incident response planning can reduce recovery costs by up to 30 percent. Incident response planning is becoming more popular as the frequency of cyber attacks rises, causing organizations to allocate more resources to training and simulations. Incident response plans may be industry-wide in the future, enabling collective resilience to cyber attacks. -
Enhanced Threat Intelligence Sharing
The exchange of information between organizations is becoming a key element in smart grid security. Platforms such as the Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs) are facilitating the sharing of real-time information between organizations to help them stay ahead of emerging threats. Information sharing between organizations has been shown to reduce the impact of attacks by up to 40 percent. Information sharing is expected to continue to evolve, with further automation to make it more efficient. -
Integration of Blockchain Technology
The technology of the blockchain is being investigated for the security of smart grids, as it provides an incorruptible record of transactions. The companies are trying out blockchain solutions to secure data exchange and increase transparency. A study showed that up to 50 percent of energy fraud could be prevented by the use of the blockchain. Future developments could lead to the use of the blockchain for secure energy trading, which would change the operating model. -
Emphasis on Physical Security Measures
Physical security for smart grids is gaining in importance as the threat of cyber attacks increases. The security of critical assets is being safeguarded with the help of surveillance, access control and physical barriers. A report has found that thirty per cent of security breaches are committed through physical access, which explains the need for a more comprehensive security strategy. Physical and cyber security measures could be combined to provide a more comprehensive security approach. -
Development of Resilient Grid Architectures
Among the challenges that are gaining attention is the design of resilient power grids to withstand cyber and physical threats. Power companies are adopting decentralized systems to enhance reliability and security. Research shows that resilient grids can reduce outages by as much as 25 per cent. But the challenge is to design and build systems that can react dynamically to threats and continue to operate.
Conclusion: Navigating Smart Grid Security Dynamics
The smart grid security market in 2023 is characterised by intense competition and a high degree of fragmentation, with both established and new players vying for market share. In the regional context, the focus is increasingly on compliance with regulations and cyber-resilience. This has prompted vendors to adjust their strategies accordingly. The established players are able to rely on their reputation and existing portfolio, while the new players are able to offer new solutions with the help of automation, artificial intelligence and sustainable development. As the market evolves, the ability to offer a flexible solution and advanced threat detection will be decisive for the vendors’ market positions. The vendors will have to prioritise these capabilities to ensure that they are able to respond to the current demands and also to the future challenges in the rapidly changing smart grid security landscape.

















Leave a Comment