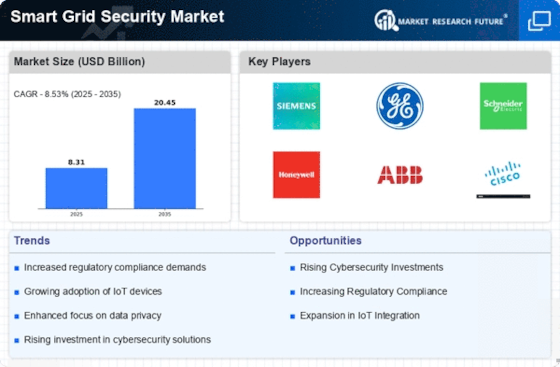
Market Analysis
Smart Grid Security market (Global, 2023)
Introduction
The security of the smart grid is a subject of increasing interest as the world's energy landscape is undergoing a profound transformation. The integration of advanced technologies and the growing demand for reliable, efficient and sustainable energy solutions are driving the smart grid security market. As energy suppliers and operators increasingly adopt smart grid systems to improve operational efficiency and enhance service delivery, the need to protect these complex, interconnected systems against cyber-attacks and physical threats has never been greater. The smart grid's unique combination of IT and operational technology raises new challenges for security and requires the development of new security frameworks that can evolve with the threat landscape. The energy industry is now beginning to recognize the importance of investing in a comprehensive security strategy that not only protects its assets but also enables compliance with regulatory standards and builds customer confidence. The development of resilient security solutions will play a crucial role in shaping the future of the smart grid and the energy sector as a whole.
PESTLE Analysis
- Political
- In 2023, the political environment of the smart grid security market will be dominated by government initiatives to increase the resilience of the energy supply system. The United States has allotted around $ 1 billion for the development of the energy sector's cyber-security as part of the Recovery, Reinvestment, and Infra-structure Act. In addition, the European Union has introduced the Cybersecurity Act, which requires all member states to implement strict security measures for all critical infrastructures, including smart grids, by 2025. This will spur investments in smart grid security solutions in the region.
- Economic
- The economic factors affecting the Smart Grid Security market are the rising costs of cyber-attacks. According to a recent industry report, by 2023, the average cost of a cyber-attack in the energy sector will be around $ 4,358,000. It is this financial burden that will force the power companies to invest more in security solutions. The smart grid security market is expected to reach $ 10 billion by the end of the year. In addition, the growing demand for clean energy is resulting in the demand for more security measures to protect these investments.
- Social
- The awareness of the public about the risks of cyber attacks has increased considerably in recent years, particularly in the context of energy security. In early 2023, a survey showed that 78% of consumers are concerned about the security of their energy supply, and 65% would be willing to pay higher electricity bills for increased security. This change in the public’s attitude is forcing energy suppliers to prioritise security investment in order to retain the public’s trust and ensure the reliability of the energy supply.
- Technological
- The smart grid security market is quickly changing due to the development of technology. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are becoming a focus of the market. By 2023, more than 40% of security solutions will integrate AI and ML to improve threat detection and response capabilities. IoT devices are being deployed more rapidly in smart grids, and the number of connected devices will reach more than 1 billion by the end of the year. The use of these devices requires a more secure IoT framework.
- Legal
- Legal aspects are increasingly influencing the market for smart grid security, especially in the context of new regulations and the requirements of conformity. In 2023, FERC issued Order 2222, which requires that the electricity companies must comply with the security standards of the smart grid. The order requires that the companies report all cyber incidents within 72 hours and thus creates a legal obligation for companies to take security measures. A penalty of up to $ 1 million per infringement was also introduced, which acted as a further stimulus for the companies to invest in smart grid security.
- Environmental
- The energy sector is increasingly influenced by the environment. In 2023, about one-third of the world's energy will come from renewable sources, which are more vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Therefore, it is increasingly necessary to develop security solutions that not only protect against cyber-attacks, but also support the integration of clean energy sources. This dual focus will lead to the development of security measures that are compatible with the environment.
Porter's Five Forces
- Threat of New Entrants
- Barriers to entry are moderate in the smart grid security market, because of the need for specialized knowledge and technology. The increasing demand for smart grid solutions may attract new players, but the established players with their established customer relationships and knowledge of the cybersecurity field pose a challenge to newcomers. In addition, the need to meet the regulatory requirements and standards of the industry may deter potential entrants.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- Suppliers’ bargaining power in the smart grid security market is relatively low. There are many suppliers of security products and services, which creates a competitive market. This means that companies in the market can easily change supplier. But suppliers with specialized technology may have somewhat higher bargaining power because of their unique offerings.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- The buyers of Smart Grid Security are in a position of considerable power. With the wide choice of suppliers, they can easily compare solutions and negotiate the best deal. The growing awareness of the risks of cyber-attack has made buyers more demanding and informed. Suppliers are responding by lowering prices and enhancing features. In addition, the large energy companies and government agencies have significant buying power, which strengthens their position.
- Threat of Substitutes
- The threat of substitutes in the smart grid security market is moderate. There are other security solutions, such as those in information technology security, but they may not fully meet the special requirements of smart grids. These solutions may become a threat if they can offer similar security at lower cost, which will force the industry to keep innovating.
- Competitive Rivalry
- Competition in the smart grid security market is very intense, driven by the presence of a large number of players and the rapid technological progress. Companies are constantly introducing new products and improving their service offerings. The urgency to address the security threats to the energy sector is further intensifying the competition, as companies seek to differentiate themselves and win the attention of potential clients.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Increasing demand for secure energy infrastructure due to rising cyber threats.
- Government initiatives and regulations promoting smart grid technologies.
- Advancements in cybersecurity technologies tailored for energy systems.
Weaknesses
- High implementation costs for advanced security solutions.
- Lack of standardized security protocols across different regions.
- Limited awareness and understanding of smart grid security among stakeholders.
Opportunities
- Growing investment in renewable energy sources requiring enhanced security measures.
- Expansion of IoT devices in energy management creating new security needs.
- Potential for partnerships between technology firms and utility companies.
Threats
- Evolving cyber threats and sophisticated attack methods targeting energy systems.
- Regulatory changes that may impact security compliance requirements.
- Competition from alternative energy solutions that may not prioritize security.
Summary
CHARACTERISTIC OF THE SMART GRID SECURITY MARKET IN 2023: Strong demand for enhanced security measures, resulting from increasing cyber threats and supportive government regulations. High costs and lack of standardization represent key market weaknesses. Opportunities lie in the investment in renewable energy and the growing use of IoT devices. Threats come from evolving cyber threats and regulatory changes. Strategic alliances and innovation in security technology will be key for stakeholders to survive in this dynamic market.

















Leave a Comment