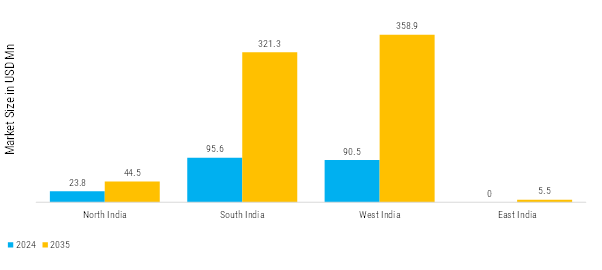
The India Wind Turbine Converters Market is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by rising performance requirements, stricter grid regulations, and a strong national push toward renewable energy expansion. This shift is particularly evident as the industry moves away from legacy converter architectures toward high-efficiency, environmentally compliant solutions such as SiC-based converters, modular multilevel converter (MMC) designs, and next-generation IGBT systems. Moreover, with the need for higher energy yield, reduced downtime, and improved reactive power and fault-ride-through performance becoming more pronounced, demand for innovative, thermally robust, and maintenance-friendly converter technologies continues to accelerate.
Furthermore, India’s surge in utility-scale wind projects, repowering of older farms, and expansion of hybrid wind-solar-storage systems is amplifying the role of converters in ensuring grid stability, enhancing turbine efficiency, and supporting seamless integration with the country’s modernizing power infrastructure.
Transition Toward Advanced Semiconductor Technologies (SiC & IGBT)
India’s wind turbine converter market is witnessing a rapid transition toward high-performance semiconductor technologies such as silicon carbide (SiC) and advanced IGBT modules. These components offer superior switching efficiency, reduced thermal losses, and enhanced reliability—critical for turbines operating in India’s widely varying climatic environments. Additionally, SiC-based converters, in particular, support higher power densities and smaller footprints, making them ideal for next-generation large-capacity turbines and offshore wind systems expected to emerge in the coming years. This shift is driven by the need for better grid compliance, improved energy capture, and extended asset life with lower maintenance overhead.
Growing Demand for Grid-Compliant and Flexible Converter Architectures
As India strengthens its grid codes, especially related to fault ride-through (FRT), harmonic control, and reactive power management, which makes the need for sophisticated converter systems has grown substantially. Modern converters such as full-scale converters (FSCs) and modular multilevel converters (MMCs) are increasingly preferred for their ability to deliver precise grid synchronization, voltage regulation, and disturbance handling. These technologies enable smooth integration of wind power into India’s evolving transmission network while ensuring minimal grid disruptions even during fluctuations or faults.
Increasing Adoption of Customized Stabilizer Blends for Streamlined Manufacturing
Digitalization is becoming a major trend as OEMs incorporate AI-enabled diagnostics, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance capabilities into converter systems. These technologies help operators detect early degradation in power electronics, optimize performance, and reduce costly downtimes. Real-time feedback loops between converters, turbine controllers, and grid systems are improving overall efficiency and enabling seamless asset management across geographically distributed wind farms.