Government Initiatives and Funding
Government initiatives aimed at combating HPV-related diseases significantly influence the HPV-associated Disorder Market. Various health organizations and governmental bodies have launched campaigns to promote HPV vaccination and screening programs. For instance, funding for vaccination programs has increased, with some countries allocating substantial budgets to ensure widespread access to HPV vaccines. This financial support not only enhances public awareness but also facilitates the development of new treatment modalities. As a result, the HPV-associated Disorder Market is likely to experience growth driven by these initiatives, which aim to reduce the burden of HPV-related disorders on healthcare systems.
Technological Innovations in Treatment
Technological advancements in treatment options are reshaping the HPV-associated Disorder Market. Innovations such as immunotherapy and targeted therapies are emerging as promising alternatives to traditional treatments. These novel approaches have shown potential in improving patient outcomes and reducing side effects. For instance, recent studies suggest that immunotherapy could enhance the body's immune response against HPV-related cancers, leading to better survival rates. As these technologies continue to evolve, they are expected to attract investment and research, thereby driving growth in the HPV-associated Disorder Market. The integration of technology into treatment protocols may also lead to more personalized care, further enhancing market dynamics.
Increasing Prevalence of HPV Infections
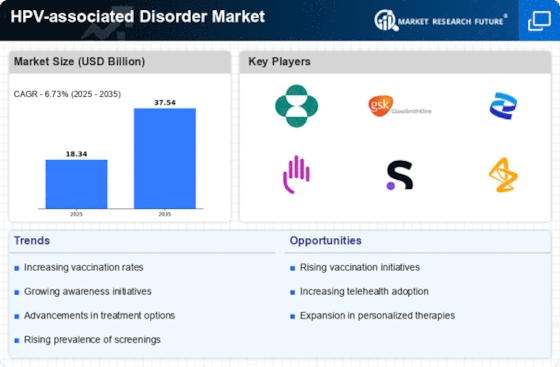
The rising incidence of HPV infections is a primary driver of the HPV-associated Disorder Market. Recent estimates indicate that nearly 80 million individuals in the United States are currently infected with HPV, with approximately 14 million new infections occurring each year. This growing prevalence underscores the urgent need for effective screening and treatment options, thereby propelling market growth. As awareness of HPV's role in various cancers, particularly cervical cancer, increases, healthcare providers are more likely to recommend preventive measures and treatments. Consequently, this trend is expected to stimulate demand for vaccines and therapeutic interventions, further expanding the HPV-associated Disorder Market.
Rising Demand for Preventive Healthcare
The increasing emphasis on preventive healthcare is a significant driver of the HPV-associated Disorder Market. As populations become more health-conscious, there is a growing demand for preventive measures, including HPV vaccination and regular screenings. This trend is particularly evident among younger demographics, who are more likely to seek vaccination as a proactive health measure. The World Health Organization has advocated for the inclusion of HPV vaccination in national immunization programs, which has led to increased uptake. Consequently, this shift towards preventive healthcare is expected to bolster the HPV-associated Disorder Market, as more individuals seek to protect themselves against HPV-related diseases.
Growing Research and Development Activities
The surge in research and development activities focused on HPV-related disorders is a crucial driver of the HPV-associated Disorder Market. Numerous pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are investing in the development of new vaccines, diagnostic tools, and therapeutic agents. Recent data indicates that R&D spending in this area has increased significantly, with several clinical trials underway to evaluate the efficacy of novel treatments. This focus on innovation not only enhances the understanding of HPV-related diseases but also paves the way for the introduction of advanced solutions in the market. As a result, the HPV-associated Disorder Market is likely to benefit from these ongoing research efforts, which aim to address unmet medical needs.