Advancements in Treatment Options
Innovations in treatment options for nontuberculous mycobacterial infections are likely to significantly impact the nontuberculous mycobacteria market. Recent developments in antibiotic therapies and combination treatments have shown promise in improving patient outcomes. For instance, the introduction of novel macrolides and other antimicrobial agents has been associated with higher success rates in treating these infections. The market is projected to grow as healthcare providers adopt these new therapies, which may lead to a reduction in treatment duration and improved patient compliance. Additionally, the potential for personalized medicine approaches in treating nontuberculous mycobacterial infections could further enhance the market landscape, as tailored therapies may yield better results for patients.
Growing Demand for Rapid Diagnostic Tools
The demand for rapid diagnostic tools for nontuberculous mycobacterial infections is on the rise, which may significantly influence the nontuberculous mycobacteria market. Healthcare providers are increasingly seeking efficient and accurate diagnostic methods to facilitate timely treatment decisions. The emergence of molecular diagnostic techniques, such as PCR and next-generation sequencing, has the potential to revolutionize the diagnostic landscape. These technologies can provide results within hours, compared to traditional methods that may take weeks. As the healthcare system in Germany continues to prioritize rapid diagnosis and treatment, the market for nontuberculous mycobacteria is likely to expand, driven by the need for innovative diagnostic solutions.
Increased Government Initiatives and Support
Government initiatives aimed at combating infectious diseases are expected to bolster the nontuberculous mycobacteria market in Germany. The German government has been actively promoting research and awareness campaigns focused on infectious diseases, which includes nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Funding allocations for research projects and public health initiatives have increased, potentially leading to advancements in diagnostics and treatment options. This support may encourage collaboration between public health organizations and private sector companies, fostering innovation in the nontuberculous mycobacteria market. As a result, the market could experience growth driven by enhanced research capabilities and improved healthcare infrastructure.
Enhanced Awareness Among Healthcare Professionals
There appears to be a growing awareness among healthcare professionals regarding nontuberculous mycobacterial infections, which could serve as a catalyst for the nontuberculous mycobacteria market. Continuous medical education programs and training sessions are increasingly focusing on these infections, leading to improved recognition and diagnosis. As healthcare providers become more knowledgeable about the clinical implications and treatment options, they may be more inclined to test for and treat these infections. This heightened awareness is likely to result in increased patient referrals and a greater demand for diagnostic and therapeutic products in the nontuberculous mycobacteria market, ultimately contributing to its growth.
Rising Incidence of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infections
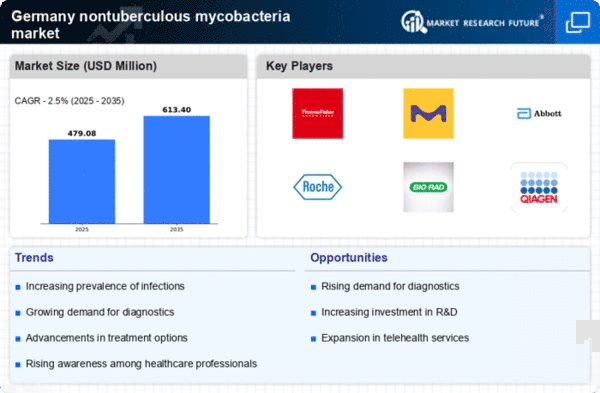
The increasing incidence of nontuberculous mycobacterial infections in Germany appears to be a primary driver for the nontuberculous mycobacteria market. Recent studies indicate that the prevalence of these infections has risen by approximately 20% over the past decade, leading to heightened demand for diagnostic and therapeutic solutions. This trend is likely to stimulate growth in the market as healthcare providers seek effective treatments and diagnostic tools. Furthermore, the aging population in Germany, which is more susceptible to such infections, may contribute to this upward trajectory. As a result, pharmaceutical companies and diagnostic manufacturers are expected to invest more in research and development to address this growing health concern, thereby expanding the nontuberculous mycobacteria market.