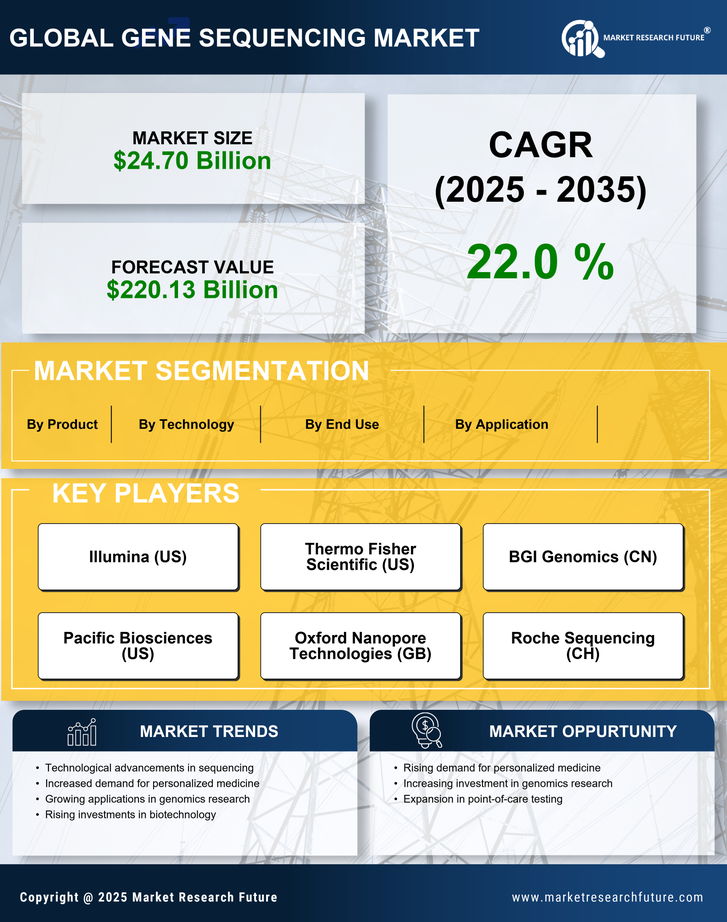
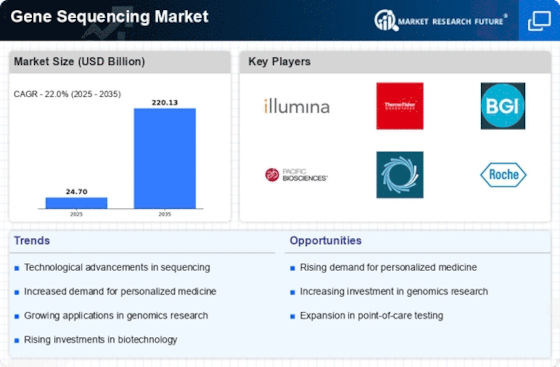
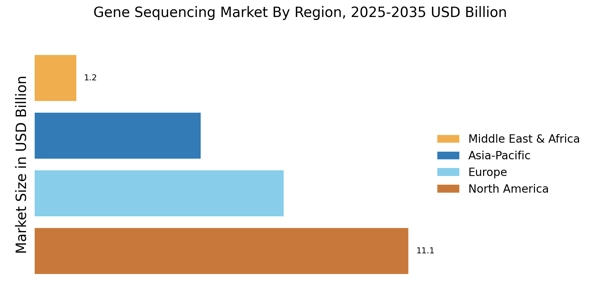
Growing Applications in Oncology
The application of gene sequencing in oncology is emerging as a major driver for the Gene Sequencing Market. With the increasing recognition of the genetic basis of cancer, sequencing technologies are being utilized to identify mutations and tailor treatments accordingly. This personalized approach to cancer therapy is gaining traction, as it allows for more effective and targeted interventions. The oncology segment of the gene sequencing market is projected to grow significantly, with estimates suggesting it could account for over 30% of the total market share by 2027. As more oncologists adopt sequencing as a standard practice in treatment planning, the Gene Sequencing Market is likely to expand rapidly, offering new hope for cancer patients.
Rising Demand for Genetic Testing
The Gene Sequencing Market is experiencing a notable surge in demand for genetic testing. This increase is largely driven by the growing awareness of genetic disorders and the importance of early diagnosis. As healthcare providers and patients alike recognize the value of genetic insights, the market is projected to expand significantly. According to recent estimates, the genetic testing segment is expected to reach a valuation of over 20 billion dollars by 2026. This trend is further fueled by advancements in sequencing technologies, which enhance the accuracy and efficiency of genetic tests. Consequently, the Gene Sequencing Market is poised for substantial growth as more individuals seek genetic testing for both health management and personalized treatment options.
Advancements in Sequencing Technologies
Technological innovations are a pivotal driver in the Gene Sequencing Market. The advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS) has revolutionized the field, enabling faster and more cost-effective sequencing processes. These advancements have led to a decrease in the cost of sequencing, making it accessible to a broader range of applications, including clinical diagnostics and research. The market for NGS is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 20% over the next few years. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in data analysis is enhancing the interpretation of sequencing results, thereby improving clinical outcomes. As these technologies continue to evolve, the Gene Sequencing Market is likely to witness unprecedented growth and innovation.
Increased Investment in Genomic Research
Investment in genomic research is a critical factor propelling the Gene Sequencing Market forward. Governments and private entities are allocating substantial funds to support research initiatives aimed at understanding genetic diseases and developing targeted therapies. For instance, funding for genomics research has seen a significant uptick, with billions of dollars being invested annually. This influx of capital is fostering collaborations between academic institutions and biotechnology companies, leading to breakthroughs in gene therapies and personalized medicine. As research continues to unveil the complexities of the human genome, the Gene Sequencing Market stands to benefit immensely from these advancements, potentially leading to new treatment modalities and improved patient outcomes.
Regulatory Support and Policy Initiatives
Regulatory frameworks and policy initiatives are playing a crucial role in shaping the Gene Sequencing Market. Governments are increasingly recognizing the importance of genomics in healthcare and are implementing policies to support its integration into clinical practice. Initiatives aimed at streamlining the approval process for genetic tests and therapies are fostering innovation and encouraging market entry. Additionally, reimbursement policies are evolving to cover genetic testing, making it more accessible to patients. This supportive regulatory environment is expected to drive growth in the Gene Sequencing Market, as it facilitates the adoption of new technologies and encourages investment in genomic research and development.