Increasing Regulatory Frameworks
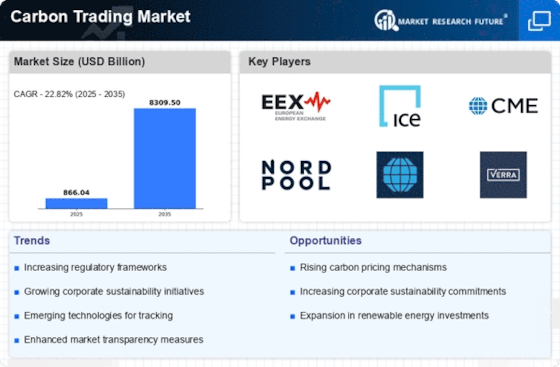
The Carbon Trading Market is experiencing a surge in regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Governments are implementing stricter emissions targets, which compel companies to participate in carbon trading schemes. For instance, the European Union Emissions Trading System has set a target to reduce emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. This regulatory pressure is likely to drive demand for carbon credits, as companies seek to comply with these regulations. Furthermore, as more countries adopt similar frameworks, the Carbon Trading Market is expected to expand, creating new opportunities for trading platforms and compliance services. The increasing complexity of regulations may also lead to a rise in consultancy services, further enhancing market dynamics.
International Climate Agreements
The Carbon Trading Market is significantly shaped by international climate agreements that set binding targets for emissions reductions. Agreements such as the Paris Accord have established frameworks for countries to commit to lowering their carbon footprints, which in turn drives the demand for carbon credits. As nations strive to meet their obligations under these agreements, the need for effective carbon trading mechanisms becomes increasingly apparent. The potential for cross-border trading of carbon credits may also emerge, allowing countries to leverage their unique emissions profiles. This dynamic could lead to a more interconnected Carbon Trading Market, fostering collaboration and innovation among participating nations. The ongoing evolution of international climate policy is likely to create both challenges and opportunities for market participants.
Corporate Carbon Neutrality Goals
The Carbon Trading Market is significantly influenced by the growing trend of corporate carbon neutrality goals. Many companies are committing to net-zero emissions by 2050, which necessitates the purchase of carbon credits to offset their emissions. According to recent data, over 1,500 companies have set science-based targets, indicating a robust commitment to sustainability. This trend is likely to increase the demand for carbon credits, thereby driving the growth of the Carbon Trading Market. As corporations strive to enhance their environmental credentials, they may invest in carbon offset projects, further stimulating market activity. The alignment of corporate strategies with sustainability goals could lead to innovative trading mechanisms and partnerships within the industry.
Technological Innovations in Carbon Tracking
Technological advancements are playing a pivotal role in the evolution of the Carbon Trading Market. Innovations in blockchain technology and artificial intelligence are enhancing the transparency and efficiency of carbon credit transactions. For example, blockchain can provide a secure and immutable record of carbon credits, which may increase trust among market participants. Additionally, AI-driven analytics can help companies better assess their carbon footprints and identify cost-effective offset strategies. As these technologies become more integrated into carbon trading platforms, they could potentially lower transaction costs and improve market accessibility. The ongoing development of these technologies is likely to attract new participants to the Carbon Trading Market, fostering a more competitive environment.
Rising Investor Interest in Sustainable Assets
The Carbon Trading Market is witnessing a notable increase in investor interest in sustainable assets. As environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria gain traction among investors, carbon credits are becoming an attractive investment option. Recent reports indicate that sustainable investment funds have seen substantial inflows, with a significant portion directed towards carbon-related assets. This trend suggests that investors are increasingly recognizing the potential for financial returns alongside environmental benefits. The influx of capital into the Carbon Trading Market may lead to enhanced liquidity and more robust trading volumes. Furthermore, as institutional investors prioritize sustainability, the market could experience a shift towards more innovative financial products linked to carbon credits.