Market Analysis
Neobanking (Global, 2025)
Introduction
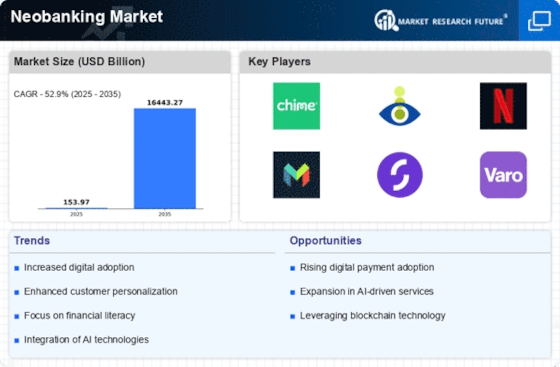
The neobanks have become a major force in the financial services sector, offering new digitally-based services that cater to the changing needs of the digitally-savvy consumer. With the need to adapt to the rapidly changing digital environment, the neobanks have risen to the challenge of offering the digitally-savvy customer a seamless, easy-to-use service that places convenience and accessibility at the forefront. This market analysis examines the key trends, competition and consumers driving the neobanks’ business strategies, as well as the strategic initiatives undertaken by different players to differentiate themselves in an increasingly crowded marketplace. The neobanks are not only redefining the banking experience with their focus on customer experience, a personal service and the integration of advanced technology, but they are also challenging the status quo of the financial institutions, thereby paving the way for a new era of banking, one that is agile, inclusive and responsive to the needs of a diverse customer base.
PESTLE Analysis
- Political
- In 2025, the Neobanking market was influenced by the regulatory frameworks of various countries. For example, the European Union introduced the Second Payment Services Directive (PSD2), which requires banks to give third parties access to customer data, affecting 500 million European citizens. Also, the United States established the Office of Financial Technology to regulate the implementation of financial technology, affecting more than 10,000 financial institutions in the country. In this way, the political environment was conducive to the development of Neobanking and ensured the security of customers.
- Economic
- The Neobanks’ economic environment in 2025 is characterised by a growing demand for digital financial services, with some 75% of consumers preferring the services of an Internet bank to those of a traditional bank. The global digital payments market is expected to reach 10 trillion dollars by then, spurred on by the 80% penetration of the population with mobile phones. This economic trend represents a considerable opportunity for Neobanks to increase their share of the financial services market, as consumers seek more convenience and lower charges.
- Social
- The social trend in 2025 is a strong trend towards financial inclusion, with the Neobanks concentrating on the underbanked. The Neobanks are concentrating on the unbanked, a population that stands at a billion and a half. A survey shows that sixty per cent of millennials and Gen Z consumers prefer to bank with digital-first institutions, indicating a cultural shift towards financial solutions that are technologically based. This social inclination towards Neobanking is changing customer expectations and driving innovation in the delivery of financial services.
- Technological
- Moreover, the development of artificial intelligence and machine learning has become a major feature of the neobanks, allowing them to offer better customer service and better fraud detection. It is estimated that by 2025, about ninety per cent of neobanks will use artificial intelligence-based chatbots to improve their customer service and cut costs. Also, the implementation of the blockchain technology will allow them to reduce costs and make operations more secure and transparent, thereby increasing trust and the speed of financial transactions.
- Legal
- The legal framework in 2025 is shaped by strict requirements for compliance. For example, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) has established guidelines for all financial institutions, including Neobanks, that are required to implement anti-money laundering (AML) measures, and these guidelines apply to more than 200 jurisdictions around the world. Also, data protection regulations such as the European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) impose strict penalties for noncompliance, with fines of up to 20 million or 4 percent of global turnover, which means that Neobanks have to place a high priority on the security of their data and compliance with regulations.
- Environmental
- In 2025 the Neobanks will have to take more and more account of the environment. The consumers will demand sustainable banking practices. A survey shows that 70% of consumers are prepared to change bank to a bank which is committed to the environment. The Neobanks have already adopted some green policies, such as carbon-offsetting schemes and the promotion of paperless transactions. The market for green finance is expected to grow to 5 trillion by 2025. The Neobanks will have to offer green products and services to attract the consumers who are concerned about the environment.
Porter's Five Forces
- Threat of New Entrants
- The market for neobanks in 2025 is likely to see a moderate threat from new entrants. The low operating costs of digital banks, the increasing demand for online financial services and the regulatory barriers to entry deter new entrants. Also, the established neobanks and the traditional banks that have entered the digital world may limit the way new entrants can operate.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- In the neobanking sector the bargaining power of the suppliers is relatively low. They mainly rely on technology suppliers, payment system operators, and data-analytics companies, of which there are many. These suppliers are in competition with one another, and this competition is advantageous to the neobanks. The suppliers have less influence on the price or quality of the service.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- The bargaining power of buyers is high in the Neobanking market because customers have a lot of options to choose from. If they find better interest rates, features or customer service at a competitor, they are free to switch. This forces Neobanks to offer new and better services to retain their customers.
- Threat of Substitutes
- The threat of substitutes in the market for new banks is medium. While there are still banks that offer similar services, the rise of fintech companies offering alternative financial solutions such as P2P lending and crypto-currency platforms is a challenge. The unique value propositions of new banks, such as lower costs and better customer experience, help to reduce this threat.
- Competitive Rivalry
- Competition is high in the neobanking sector, with many players competing for market share. The industry is characterised by aggressive marketing, constant innovation and the introduction of new features to attract customers. In addition, the growing number of established neobanks and traditional banks entering the digital space has intensified competition, resulting in price wars and increased investment in technology and customer service.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Lower operational costs compared to traditional banks due to digital-only infrastructure.
- Enhanced customer experience through user-friendly interfaces and personalized services.
- Rapid innovation and adaptability to changing consumer preferences and technology trends.
Weaknesses
- Limited brand recognition and trust compared to established banks.
- Regulatory challenges and compliance issues in various markets.
- Dependence on technology which may lead to vulnerabilities in cybersecurity.
Opportunities
- Growing demand for digital financial services among tech-savvy consumers.
- Expansion into emerging markets with underbanked populations.
- Partnerships with fintech companies to enhance service offerings and reach.
Threats
- Intense competition from both traditional banks and other fintech startups.
- Potential regulatory changes that could impact operational models.
- Economic downturns that may affect consumer spending and investment in digital banking.
Summary
In 2025, the Neobanking market will be characterized by cost efficiency and customer-centric services. The main challenge will be brand trust and regulatory compliance. Strategic alliances and the expansion of digital services in emerging markets will be the main growth opportunities. Competition and the regulatory environment will be the main threats. Proactive innovation and risk management will be essential.

















Leave a Comment