Increasing Renewable Energy Integration
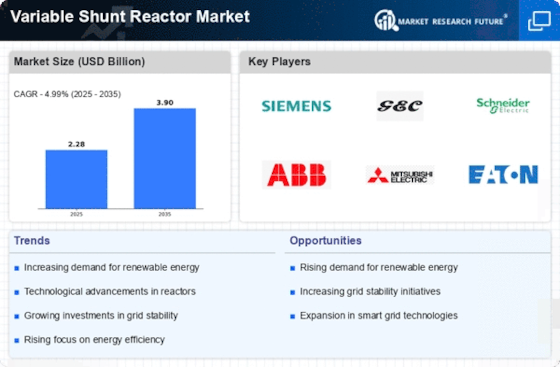
The Variable Shunt Reactor Market is experiencing a notable surge due to the increasing integration of renewable energy sources into power grids. As countries strive to meet ambitious renewable energy targets, the demand for technologies that can manage voltage fluctuations and enhance grid stability becomes paramount. Variable shunt reactors play a crucial role in this context, as they can effectively mitigate the intermittent nature of renewable energy generation. According to recent data, the share of renewables in the energy mix is projected to reach 50% by 2030, necessitating advanced solutions like variable shunt reactors to ensure reliable power delivery. This trend indicates a robust growth trajectory for the Variable Shunt Reactor Market, as utilities and grid operators seek to enhance their infrastructure to accommodate a higher percentage of renewable energy.
Rising Demand for Power Quality Improvement
The Variable Shunt Reactor Market is significantly influenced by the rising demand for power quality improvement across various sectors. As industrial and commercial entities increasingly rely on sensitive electronic equipment, the need for stable voltage levels and reduced harmonic distortion has become critical. Variable shunt reactors are instrumental in achieving these objectives, as they can dynamically adjust reactive power compensation. Market data suggests that The Variable Shunt Reactor Market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of over 6% in the coming years. This growth is likely to drive the adoption of variable shunt reactors, as industries prioritize investments in technologies that enhance power quality and operational efficiency.
Expansion of Transmission and Distribution Networks
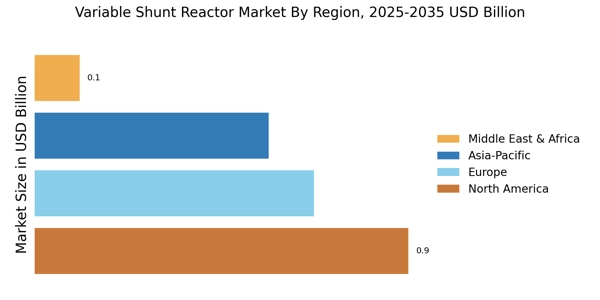
The Variable Shunt Reactor Market is poised for growth due to the ongoing expansion of transmission and distribution networks. As urbanization and population growth continue to escalate, the demand for reliable electricity supply is intensifying. This expansion necessitates the deployment of advanced technologies, including variable shunt reactors, to manage voltage levels and ensure efficient power flow. Recent statistics indicate that investments in transmission and distribution infrastructure are projected to exceed USD 300 billion annually over the next decade. This substantial investment is likely to create a favorable environment for the Variable Shunt Reactor Market, as utilities seek to enhance grid reliability and accommodate increasing electricity demand.
Supportive Regulatory Frameworks for Energy Transition
The Variable Shunt Reactor Market is increasingly supported by regulatory frameworks aimed at facilitating the energy transition. Governments worldwide are implementing policies that promote energy efficiency and the adoption of low-carbon technologies. These regulations often include incentives for utilities to invest in reactive power management solutions, such as variable shunt reactors. Recent legislative measures in various regions indicate a commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing grid resilience. This supportive regulatory environment is likely to drive investments in the Variable Shunt Reactor Market, as utilities align their strategies with national and international energy goals.
Technological Innovations in Reactive Power Management
The Variable Shunt Reactor Market is benefiting from technological innovations in reactive power management. Advances in control systems and materials have enhanced the performance and efficiency of variable shunt reactors, making them more attractive to utilities and grid operators. These innovations allow for better integration with smart grid technologies, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustment of reactive power levels. As the market for smart grid solutions continues to expand, the demand for advanced reactive power management technologies, including variable shunt reactors, is expected to rise. This trend suggests a promising outlook for the Variable Shunt Reactor Market, as stakeholders seek to leverage cutting-edge technologies to optimize grid performance.