Rising Awareness and Advocacy
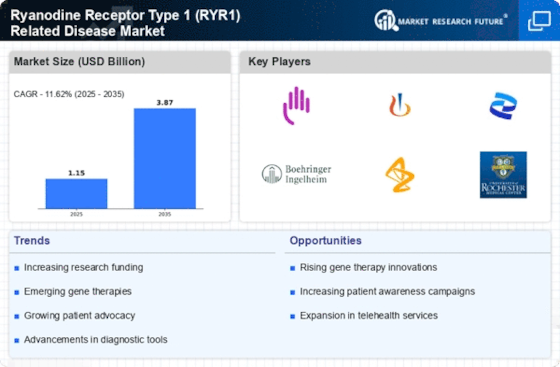
The increasing awareness and advocacy surrounding RYR1 related diseases are driving growth in the Ryanodine Receptor Type 1 (RYR1) Related Disease Market. Patient advocacy groups and healthcare organizations are actively working to educate the public and medical community about these conditions, which has led to heightened recognition of symptoms and the importance of early diagnosis. This growing awareness is likely to result in more individuals seeking medical attention, thereby increasing the demand for diagnostic and therapeutic solutions. Additionally, advocacy efforts may influence funding and research priorities, further propelling advancements in the Ryanodine Receptor Type 1 (RYR1) Related Disease Market.
Advancements in Genetic Testing
The evolution of genetic testing technologies is significantly influencing the Ryanodine Receptor Type 1 (RYR1) Related Disease Market. Enhanced genetic testing methods, including next-generation sequencing, allow for more accurate and timely diagnosis of RYR1 related diseases. This advancement not only aids in identifying at-risk individuals but also facilitates personalized treatment approaches. As genetic testing becomes more accessible and affordable, it is expected that the number of diagnosed cases will increase, thereby expanding the market. Furthermore, the integration of genetic testing into routine clinical practice may lead to earlier interventions, improving patient outcomes and driving demand for targeted therapies within the Ryanodine Receptor Type 1 (RYR1) Related Disease Market.
Growing Investment in Research and Development
The surge in investment directed towards research and development in the field of RYR1 related diseases is a crucial market driver. Pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are increasingly allocating resources to explore novel therapeutic options and improve existing treatments. This trend is evidenced by the rising number of clinical trials focused on RYR1 related conditions, which have seen a significant uptick in recent years. The commitment to innovation is likely to yield new drugs and therapies, enhancing the treatment landscape for patients. As a result, the Ryanodine Receptor Type 1 (RYR1) Related Disease Market is poised for growth, driven by the introduction of advanced treatment modalities that address the complexities of these diseases.
Increasing Prevalence of RYR1 Related Diseases
The rising incidence of Ryanodine Receptor Type 1 (RYR1) related diseases, such as malignant hyperthermia and central core disease, is a pivotal driver for the Ryanodine Receptor Type 1 (RYR1) Related Disease Market. Recent estimates suggest that these conditions affect a notable percentage of the population, with malignant hyperthermia occurring in approximately 1 in 15,000 anesthetic exposures. This increasing prevalence necessitates enhanced diagnostic and therapeutic options, thereby propelling market growth. As awareness of these diseases expands among healthcare professionals and patients, the demand for specialized treatments and interventions is likely to rise. Consequently, pharmaceutical companies are investing in research and development to address these unmet medical needs, which could further stimulate the Ryanodine Receptor Type 1 (RYR1) Related Disease Market.
Regulatory Support for Rare Disease Treatments
Regulatory bodies are increasingly providing support for the development of treatments targeting rare diseases, including those associated with RYR1. Initiatives such as orphan drug designations and expedited review processes are designed to encourage pharmaceutical companies to invest in therapies for conditions that may otherwise be overlooked. This regulatory environment fosters innovation and can lead to a more robust pipeline of treatments for RYR1 related diseases. As companies navigate these supportive frameworks, the Ryanodine Receptor Type 1 (RYR1) Related Disease Market is likely to benefit from a more diverse array of therapeutic options, ultimately improving patient access to necessary treatments.