Acute Pulmonary Edema Is Always An Emergency
When Every Breath Counts: Why Acute Pulmonary Edema Is a Medical Emergency
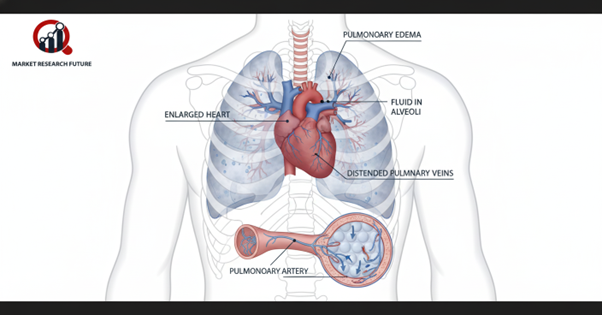
Breathing is something that most people take for granted—until it becomes a struggle. Acute pulmonary edema is one of those conditions where every breath suddenly feels like a struggle. This life-threatening emergency occurs when fluid rapidly fills the lungs, making it nearly impossible for oxygen to reach the bloodstream. Without prompt medical care, it can become life-threatening in a matter of minutes.
What Exactly Is Pulmonary Edema?
Pulmonary edema is the medical term for fluid accumulation in the lungs, which means they cannot adequately perform the gas exchange necessary for breath. This fluid prevents the lungs from filling with air, causing breathlessness, coughing, and a sense of impending doom.
There are two main types of pulmonary edema.
- Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema: This type is a consequence of heart failure and is a heart condition.
- Non-Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema: This type is a consequence of infections, severe trauma, kidney disease, high altitude, or certain drugs.
Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
Pulmonary edema can suddenly occur or develop over time. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of the condition can save a life.
What are the Common signs?
- Feeling like you cannot breathe as well as you can when you are flat on your back
- A cough that doesn't go away and may have sputum that is pink and foamy
- Feelings of tightness or pain in the chest
- Wheezing and feeling like you are struggling to breathe
- Feeling extreme tiredness and being unable to be still
- Feeling swelling in the legs and ankles or in the stomach (especially in heart-related cases)
If you or someone you know suffers from sudden difficulty with breathing, you must get medical help straight away.
How are people with Pulmonary Edema diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually starts with listening to the chest and getting a brief health history, followed by necessary tests to find the cause and severity.
Important tests are:
- A chest X-ray or chest CT scan to see if there is a blocking of the lungs and if the lungs have enlarged.
- An echocardiogram is used to see the function of the heart.
- Blood tests to see the levels of oxygen in the blood and heart, and to assess the function of the kidneys.
- Cardiac catheterization is used to see the heart and may be used to compare the heart and blood flow.
- Pulmonary edema is a medical emergency, and the first goal is to stabilize the breathing and treat the main cause.
First steps of medical care can be:
- Use oxygen and adjust breathing rates to help the blood.
- Use diuretics (water pills) to help remove excess fluid in the body.
- Use vasodilators to take the strain off the heart and improve blood flow.
- Use ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers to improve heart problems and use to treat the underlying heart problem.
- For non-cardiogenic causes, the focus is on addressing treatments specific to infections, poisons, and traumas.
Innovations and New Treatments Pulling Their Heads Out of New Cocktails
New, focused treatments aim to pull the pulmonary edema patient out of the conventional drug spiral and into small molecules, CAR-T Cell treatments, and cell exosome therapy.
Although the incidence of fatal pulmonary edema is still high, earlier medical research, recorded incidence, and mystified medical research are saving the lives of more and more patients!
Caring For Pulmonary Edema: Daily Life and Routine
The following can help reduce the chances of pulmonary edema recurrence:
- Follow a heart-healthy diet and reduce sodium.
- Routine check-ups to keep tabs on blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Moderate exercise as recommended by the doctor.
- Do not smoke and limit your alcohol intake.
- Adhere to the prescribed heart meds.
Conclusion
Acute pulmonary edema is more than a problem to focus on the lungs; it is a race against time and the deadly clock! The speed of diagnosis and medical intervention can mean the patient lives to see another day.

Leave a Comment