Market Trends
Introduction
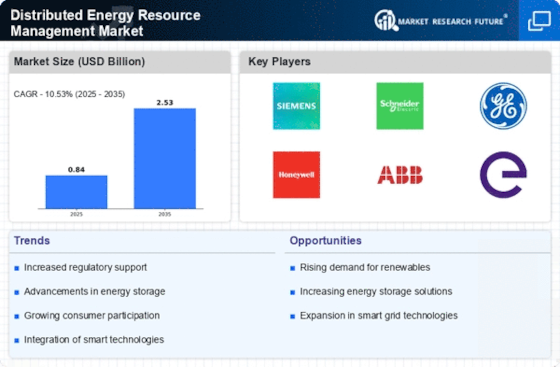
In 2024, the distributed energy resource management market is undergoing a great transformation, driven by a combination of macro-factors. In particular, technological advances in energy storage, smart grids, and IoT are reshaping the way energy is generated, distributed, and consumed. In parallel, regulatory pressures aimed at reducing CO2 emissions and promoting the adoption of renewables are driving the market towards innovation and adaptation. Furthermore, changing consumer preferences for sustainable energy solutions and greater energy management are influencing market dynamics. These trends are of critical importance to market players, as they not only highlight new opportunities but also highlight the strategic importance of aligning with the evolving market.
Top Trends
-
Increased Adoption of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are becoming increasingly important in the automation of energy management systems. These new techniques are already being used by companies like Siemens to enhance their preventive maintenance. In doing so, they are achieving a saving of up to 20 percent in operational costs. In the field of grid reliability, the public sector is also investing in the use of artificial intelligence. We expect that the next generation of these new tools will be used to improve the accuracy of energy forecasts and the responsiveness of demand-side management. -
Decentralization of Energy Systems
Local energy communities are gaining in importance. In Europe, for example, the European Union has started a program of support for local energy initiatives, resulting in a 15% increase in community solar projects. The trend is reshaping the energy system to make it more resilient and more local. In the future, the trend may lead to even more regulatory support for decentralized energy models. -
Integration of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The introduction of EVs into the power grid is transforming energy management strategies. The pioneering role played by companies such as Tesla in developing vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology is enabling EVs to act as mobile energy storage devices. V2G has the potential to reduce peak demand by up to 10 per cent at times of high consumption. EVs are becoming ever more popular, and the number of EVs on the road is rising, which will lead to even more inventive solutions to the problems of grid stability and energy distribution. -
Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures
With the increasing digitalization of energy systems, cyber security has become a matter of great importance. Industry leaders are investing heavily in advanced security systems to protect against cyber attacks, and are putting aside an estimated 30 per cent of their budgets for this purpose. Governments are also tightening the rules to ensure the security of critical energy infrastructure. There may be more developments in the future with regard to the response to and recovery from cyber attacks. -
Focus on Energy Storage Solutions
Managing intermittent energy sources is becoming a major challenge for the energy industry. The energy storage solutions developed by companies such as Enphase Energy can stabilize the grid by up to 25 percent. In order to support the integration of renewables, governments are promoting energy storage. Moreover, as technology improves, the cost of storage will decrease, enabling it to become more widely available. -
Regulatory Support for Renewable Energy
A growing number of countries are promoting the use of renewable energy sources, and many governments have set ambitious carbon-neutral goals. By way of example, in the United States, the capacity of renewable energy has increased by 40 per cent since 2007, thanks to a supportive policy framework. This trend is fostering investments in decentralized energy resources, which are contributing to a more sustainable energy system. Future policy frameworks may accelerate the transition to clean energy. -
Rise of Smart Grids
A smart grid is a new technology that allows for the analysis of real-time data and improved communication between the components of the grid. Companies such as Schneider Electric have already deployed smart grid solutions that can increase the operating efficiency of the grid by 15 percent. The smart grid is being developed with government support to facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources. In the future, it may be possible to develop still more advanced grids that facilitate the decentralised management of energy. -
Consumer Empowerment through Energy Management Systems
Energy management systems are increasingly being used by consumers to monitor their energy consumption. By means of the platforms developed by companies such as Salesforce, they are able to optimize their energy use, thus saving up to 10 per cent on their energy bills. This trend is promoting greater consumer engagement in energy management. This will in turn lead to the development of more individualized energy solutions. -
Collaboration Across Sectors
The development of distributed energy resources requires close collaboration between the energy suppliers, the technology companies and the government. These collaborations, such as the Clean Energy Ministerial, will foster innovation and investment. The result of this approach is an increase of 25% in the number of joint projects to increase energy efficiency. The next collaborations should focus on combining the most promising new technologies for maximum impact. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Practices
Energy management is increasingly based on the principles of sustainable development, and companies are implementing the principles of the circular economy. For example, GE is introducing a blade-recycling programme for its wind-turbines that will reduce waste by up to 30 per cent. Governments are also encouraging sustainable practices by means of tax breaks. Awareness of the circular economy will grow as the years go by, and the energy system will be increasingly based on it.
Conclusion: Navigating the Distributed Energy Landscape
The market for distributed energy resources is characterized by intense competition and considerable fragmentation, with the participation of both established and new players. Regionally, the focus on sustainability and regulatory support, especially in North America and Europe, is influencing the strategies of the suppliers. The established suppliers are able to use their existing network structures and integrate advanced capabilities such as automation and artificial intelligence to improve the efficiency of their operations. In contrast, the new suppliers are focusing on flexibility and innovation to capture niche markets. As the landscape evolves, the ability to implement artificial intelligence, automation, and a sustainable approach will be essential for the suppliers that want to establish themselves as market leaders.

















Leave a Comment