Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Using Right Ways to address Consumer Concerns
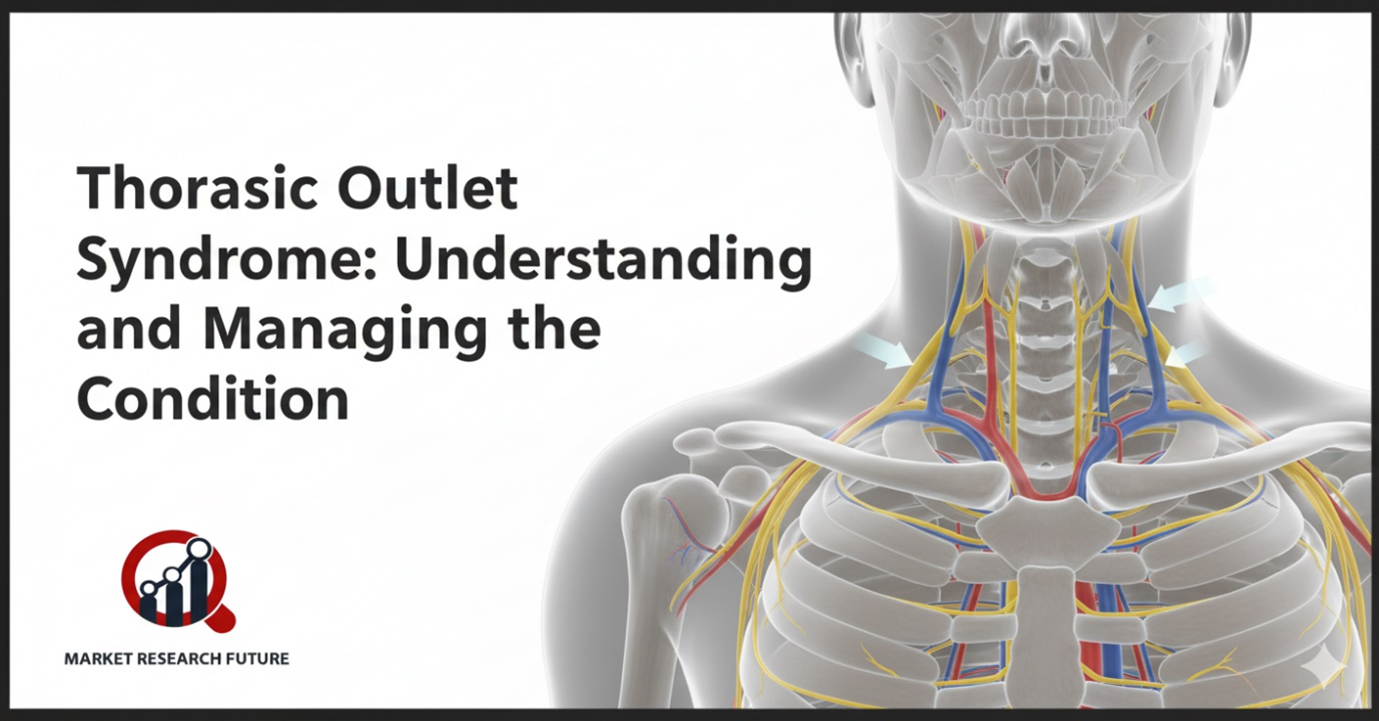
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a condition that makes the neck, shoulder, arm, and hand hurt, bulge, and feel weak. It happens when the nerves or blood arteries in the thoracic outlet, the area between your collarbone and first rib, get squished. Symptoms might be anything from slight discomfort to long-lasting, severe pain.
Who can be affected by Thoracic Outlet Syndrome?
Anyone can get TOS, but it commonly happens after an injury, repeated strain, surgery, or even pregnancy. Usually, it only affects one side of the body, but in rare circumstances, both sides might be affected. Some things that can increase your risk are being overweight, having bad posture, and doing a lot of physical exercise.
Identifying the Signs of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Persistent discomfort, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness are common symptoms. Resting the arm may help with the pain, but moving it will make it worse. It can be hard to figure out what's wrong because TOS has symptoms that are similar to those of arthritis, cervical spine diseases, and repetitive strain injuries. To confirm TOS, doctors usually employ a mix of physical tests, imaging, and diagnostic criteria.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Choices for Treatment
How bad the problem is will affect how it is treated. Physical therapy can help mild instances get better by strengthening muscles and restoring normal movement. Muscle relaxants or over-the-counter drugs may help with pain. In really bad cases, surgery may be needed to alleviate pressure on nerves or blood vessels and get rid of scar tissue. Early intervention makes things better and lowers the chance of long-term problems.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome and the Future
The need for effective TOS therapies is expanding as the population ages and more people learn about musculoskeletal problems. Improvements in minimally invasive surgery and physical therapy are making care easier and more successful.
Final Thoughts
Thoracic outlet syndrome is hard to deal with, but it is possible. Early diagnosis, changes to your daily routine, and tailored treatment can help a lot with pain and get you moving again. Patients can take charge of their health, enhance their quality of life, and avoid long-term problems by learning about risk factors and treatment alternatives.

Leave a Comment