
Regulatory Landscape - Overview
Radiopharmaceuticals Regulatory Landscape: Product Overview
Radiopharmaceuticals are the specialised class of biopharmaceuticals combining the radioactive isotopes with biological molecules and utilised for medical applications. Different types of radiations, produced by radioisotopes are used to diagnose or treat several medical conditions. It is administered to patient either by mouth or injection and can be monitored, analysed with external medical devices.
According to one of the research study published in Natures journal, around 67 radiopharmaceuticals are approved worldwide, out which 54 are utilised for disease diagnosis and 13 are used as therapeutics in treatment of various diseases.
Regulation of radiopharmaceuticals ensures if they are manufactured and distributed in compliance with safety and quality standards, which helps to ensure that radiopharmaceuticals are safe and effective for use medicine.
Radiopharmaceutical Types
Radiopharmaceuticals are segmented into diagnostic and therapeutic type. Diagnostic pharmaceuticals are used for imaging and detecting diseases in organs and tissues. Therapeutic pharmaceuticals are used for treating diseases, primarily cancer.
Radiopharmaceuticals Applications
Radiopharmaceuticals are mainly utilised for the treatment and diagnosis of malignant cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular disease, and other diseases (such as nephrotic syndrome and hepatopulmonary syndrome). They are used for producing images of organs or tissues of patient suffering with particular disease, A gamma camera is type of medical device, which detect gamma rays emitted by the radioisotope, generating images in a non-invasive way, which help to determine or reflect the function of the organ or tissue under investigation.
One of the most widely used radioisotopes in nuclear medicine is technetium-99m, which can be made the adhere to several specific molecules, for diagnosing many diseases, like certain type of cancers. For instance, technetium-99m-MDP (methylene diphosphonate) is mostly used for detecting bone metastasis associated with cancer.
Tests like positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT), which are crucial in the treatment of chronic illnesses, make use of nuclear substances for diagnostic and evaluation purposes.
Theranostics means combination of therapeutics and diagnostics and theranostics involving the use of radiopharmaceuticals are called as radiotheranostics, in which same molecule is used for first imaging and then for therapy by conjugating therapeutic radionuclides, for targeting the lesions examined they contribute to development of personalised medicine as diagnostic molecule helps to refine the treatment for each individual patient. FDA in 2016 and 2018 has approved Ga-DOTA-TATE and Lu-DOTA-TATE for the treatment and diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumors, later in 2022 Lu-PSMA-617, was approved for metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer treatment.
11 radiopharmaceuticals are approved for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD), neurodegenerative disorders which are related to high morbidity among the elderly population, including [123I] FP-CIT/[99mTc] TcHMPAO for SPECT scanning and [18F] flutemetamol/[18F] florbetapir for PET scanning.
Radiopharmaceuticals Product Development Steps:
Federal agencies like Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in US and European Medicines Agency (EMA) in European Union are involved in the regulation process of radiopharmaceuticals ensuring the safety and efficacy of this therapeutics. They play important role in the review and approval of new radiopharmaceuticals and are responsible for monitoring safety and efficacy of existing products. They even oversee the manufacturing and distribution of radiopharmaceuticals, ensuring compliance with safety and quality standards.
Furthermore, authorities like Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) in the US and Euratom Treaty in the EU, are responsible for governing the specific regulations for ensuring the safe use and disposal of these radioactive materials, including radiopharmaceuticals.
| Regulatory framework of FDA | Regulatory framework of EMA |
| Radiopharmaceuticals undergo NDA process, supervised by FDAs Centre for drug evaluation and research (CDER). | Radiopharmaceuticals undergo centralised authorisation process before the marketing of the product under EMA. |
| FDA and NRC together are responsible for the regulation and development of radiopharmaceuticals. | EMA and EC are responsible for the regulation and development of the radiopharmaceuticals. |
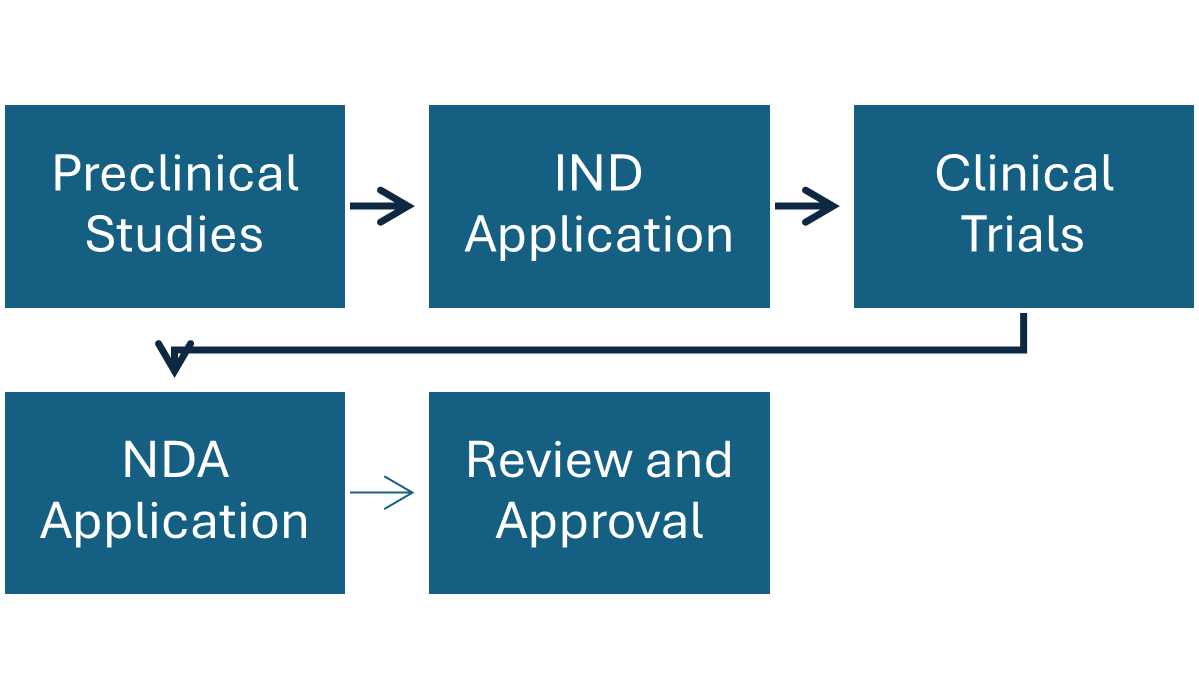
Fig: Overview of Regulation and development of Radiopharmaceuticals
Radiopharmaceuticals Market Trends
In October 2023, Nucleus RadioPharma received $56 million in funding from Eclipse and GE HealthCare in a Series A funding round. Nucleus RadioPharma is the first organization to fully integrate the development, manufacture, and supply chain of Radiopharmaceuticals. Additional investors in the project included Echo Global, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Granger Management, Mayo Clinic, Mercy Health, and the University of Missouri.
August 2023, Telix Pharmaceuticals Limited's Radiopharmaceuticals production plant in Belgium, Telix Manufacturing Solutions, officially opened in August 2023. According to the firm, their 2,800-square-meter building is one of the largest Radiopharmaceuticals production facilities in Europe. For patients in the EMEA region and beyond, this facility will be Telix's principal radioisotope and commercial/clinical product production hub. After considerable renovation, during which two cyclotrons were safely decommissioned, the facility's license to generate a wide variety of radioisotopes was renewed, allowing it to support the company's R&D, commercial, and clinical endeavours.
Radiopharmaceuticals Market Size Overview:
Radiopharmaceuticals Market Valued at USD 6.5 billion in 2023, projected to grow from USD 7.1 billion in 2024 to USD 13.10 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 9.10% during the forecast period (2024 - 2032). One of the key market driver for the growth of the market is the rising prevalence of acute and chronic diseases like cancer throughout the world as a result of numerous factors.
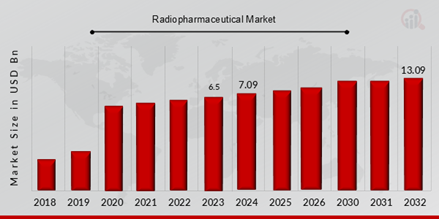
Source Secondary Research, Primary Research, MRFR Database, and Analyst Review
Radiopharmaceuticals Regulatory Landscape:
There are several key regulatory agencies who oversee the approval and monitoring of Radiopharmaceuticals to ensure their safety, efficacy, and quality.
| Regulatory agencies | Regulatory Ministry |
| Federal Food and Drug Administration | United States: Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) |
| The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency | United Kingdom: The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) under the Department of Health and Social Care (DHSC) |
| Central Drug Standard Control Organization | India: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare |
| South African Health Products Regulatory Authority (SAHPRA) | National Department of Health. |
| Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) | Japan: Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. |
| National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) | China: The Ministry of Health |
| Health Sciences Authority | Singapore: The Ministry of Health |
| European Medicine Agency | European union |
| Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency (Anvisa) | Ministry of Health, part of the Brazilian National Health System (SUS) |
Radiopharmaceuticals Guidelines:
Eligibility: Radiopharmaceutical therapy is used as a safe and effective targeted approach for treating various types of cancers, it is also seen to be effective for treatment of neuroendocrine tumors, whereas its use is avoided for pregnant women to prevent the exposure of radiation to developing fetus, even breastfeeding mothers are not recommended the administration of these therapeutics as they have the chance to be excreted out from breast milk which can be harmful to the infants. Its use in medical treatment is carefully done as the ionizing radiation can cause adverse effects of the treatment. The cost and complexity of radiopharmaceuticals can make them a later-line treatment option in some cases.
Radiopharmaceuticals Classification of the Product:
Radiopharmaceuticals Regulatory Process Overview, By Country:
US FDA Regulation for Radiopharmaceuticals
In US FDAs centre for drug evaluation and research (CDER) is responsible for regulation, review, approval of radiopharmaceuticals, they go through a strict process of NDA before marketing which includes preclinical and clinical testing, as well as manufacturing and quality control inspections. Additionally Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), is involved in ensuring safety of radioactive materials use in medicine. Radiopharmaceuticals also need to show compliance with Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations to ensure the safety, quality, and efficacy of radiopharmaceuticals during the manufacturing process. Code of federal regulations (21 CFR Part 212) has laid down specific requirements for manufacturing radiopharmaceuticals, including the use of radioactive materials, quality control, and labelling, moreover, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 10, Part 35 part of the CFR contains the regulations for the possession and use of radioactive materials in medicine. FDA has issued guidance documents on different aspects of the regulation of radiopharmaceuticals, which include the development, approval, and post-approval surveillance of these products.
Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC)
It is a federal agency in the US, responsible for regulating the safe usage and disposal of radioactive materials, including radiopharmaceuticals. The NRC’s role in regulating radiopharmaceuticals includes issue of licenses to the organizations for use or possess of radioactive materials, like radiopharmaceuticals, which specify the types and amounts of radioactive materials which can be used or possessed, even specify the conditions in which they can be used.
They conduct inspections of organizations using or possessing radioactive materials for ensuring compliance with the conditions mentioned in the issued licenses, reviewing the safety and security procedures, radiation protection programs, and emergency response plans.
The NRC is also involved in enforcement of regulations associated with use and disposal of radioactive materials, like radiopharmaceuticals. They act against organizations, violating regulations and issue fines or revoking licenses for non-compliance.
They regulate radiopharmaceuticals disposal system, by approving, monitoring the disposal sites for ensuring that radioactive waste is stored properly, transported and disposed without any harm to the public and the environment. The NRC also looks after and prevent any malicious use radioactive materials.
EMA guidelines for regulation of Radiopharmaceuticals
In European Union, European Medicines Agency (EMA) and European Commission (EC) is responsible for Radiopharmaceuticals. EU Guidelines on GMP for medicinal products and EU Guidelines on Good Clinical Practice (GCP) for clinical trials ensures the safety, quality, and efficacy of radiopharmaceuticals during the manufacturing process. Radiopharmaceuticals governed under EMA undergo centralised authorisation process. Additionally, the use of radiopharmaceuticals is also regulated by the EU Basic Safety Standards Directive and the EU Directive on the protection of workers from the risks related to ionizing radiation EMA scientific guideline on radiopharmaceuticals This guideline describes the specific additional information that needs to be submitted in relation to radiopharmaceuticals, in the context of applications for marketing authorisations or variations to authorised medicinal products.
Euratom Treaty
The Euratom Treaty regulates the use of radioactive materials, including radiopharmaceuticals, in the EU. Their main goal is ensuring the health of workers and the general public from harm due to ionizing radiation, by setting limits for ionising radiation exposure, forming protocols for monitoring compliance for this limits. They are involved in inspection and enforcement of standards of safety for using these radioactive materials, ensuring compliance with regulations. Furthermore, they encourage research and development in field of radiation protection and the safe use of radioactive materials, including radiopharmaceuticals and establish regulatory guidelines for management of radioactive waste and its disposal for ensuring protection of environment and public health.
US FDA approved Radiopharmaceuticals are as follows:
March 2024, The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Lantheus' DEFINITY (Perflutren Lipid Microsphere) supplemental new drug application (sNDA) for use as an ultrasound-enhancing agent in pediatric patients with subpar echocardiograms.
April 2022, Curium Announces FDA Approval of a Generic Version of DaTscan (Ioflupane I 123 Injection) in the U.S. Ioflupane I 123 Injection is a single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) brain imaging agent used to assist in the evaluation of adult patients with suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes.
Radiopharmaceuticals Regulatory Challenges:
Lengthy regulatory approval process: Gaining regulatory approval for new radiopharmaceuticals is a strict, long and complex process which can delay the product launch by the companies in a timely manner, and it can also make it difficult for patients to access new treatments.
Safety and Quality Control: Ensuring the safety and efficacy of radiopharmaceuticals is major challenge and regulatory bodies like the FDA, EMA, and IAEA has issued strict regulatory framework for the manufacturing, handling, and disposing these substances, protecting patients, healthcare workers, and the surrounding environment.
Ethical and Environmental Concerns: The use of radiopharmaceuticals, raises ethical and environmental issues. Proper disposal and management of radioactive waste is major challenge to prevent contamination and ensuring public safety.
Short Half-Lives: many radiopharmaceuticals have short half-lives, which can complicate their production, distribution, and use, requiring precise coordination and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for ensuring their efficacy when administered.
Complex Regulatory Frameworks: varying regulations are seen in Different countries, posing manufacturing challenge for the company at international level. Compliance with diverse regulatory requirements requires a complete understanding of each region's specific guidelines.
Possible Risk in the development of Radiopharmaceuticals
Cost of development: Development of new radiopharmaceuticals is costly and time-consuming process. Significant cost is required for the preclinical and clinical trials, and manufacturing, distributing process of radiopharmaceuticals, making it difficult companies and academic institutions to develop new radiopharmaceuticals.
Need for more specific and sensitive radiopharmaceuticals: need for more specific and sensitive radiopharmaceuticals, better targeting specific diseases and providing more detailed information about the condition.
Limited availability of certain isotopes: few isotopes, such as certain positron emitters, are only available in limited quantity, making it difficult for manufacturing and utilizing these radiopharmaceuticals on a large scale.
Radiopharmaceuticals Competitive Landscape Dashboard:
Companies With Marketed Radiopharmaceuticals Products:
- GE Healthcare
- Lantheus Medical Imaging Inc.
- BWX Technologies Inc.
- Siemens Healthineers
- IRE ELiT
- JSC Isotope
- Novartis AG
- NTP Radioisotopes SOC Ltd
- Curium
- Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organization (ANSTO)
Regulatory Landscape - Table of Content
Table of contents will appear here once available.
Customer Stories

“This is really good guys. Excellent work on a tight deadline. I will continue to use you going forward and recommend you to others. Nice job”

“Thanks. It’s been a pleasure working with you, please use me as reference with any other Intel employees.”

“Thanks for sending the report it gives us a good global view of the Betaïne market.”

“Thank you, this will be very helpful for OQS.”

“We found the report very insightful! we found your research firm very helpful. I'm sending this email to secure our future business.”

“I am very pleased with how market segments have been defined in a relevant way for my purposes (such as "Portable Freezers & refrigerators" and "last-mile"). In general the report is well structured. Thanks very much for your efforts.”

“I have been reading the first document or the study, ,the Global HVAC and FP market report 2021 till 2026. Must say, good info! I have not gone in depth at all parts, but got a good indication of the data inside!”

“We got the report in time, we really thank you for your support in this process. I also thank to all of your team as they did a great job.”