
Regulatory Landscape - Overview
Peptide Drugs Regulatory Landscape: Product Overview
Peptides are short chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds, typically made up of 2 to 50 amino acids, they can be generated both naturally in the body and chemically in laboratories. Natural peptide synthesis occurs by ribosomal translation, in which messenger RNA (mRNA) directs the assembly of amino acids into peptide chains. Synthetic peptides, on the other hand, are created using processes like solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) or liquid-phase synthesis, which enable exact control over amino acid sequences.
Peptides can be classified based on their length into Dipeptides (Composed of two amino acids), Tripeptides (Composed of three amino acids), Oligopeptides (Typically consisting of 4 to 20 amino acids), Polypeptides (Chains of more than 20 amino acids, often considered to be proteins if they exceed a certain size).
They are gaining popularity in medicine research because they show precise or selective response and having less negative effects than typical small molecule therapies. And can be tailored to target specific biological pathways, making them useful for treatment of variety of diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Peptide-based vaccines are also being investigated for their ability to stimulate immune responses against specific diseases.
FDA point A total of nine TIDES (pepTIDES and oligonucleoTIDES) were approved by the FDA during 2023 accounting 16% of all approved drugs, surpassing, 14% approvals in 2022. Out of which 5 were peptide drugs and FDA has granted its first orphan drug designation for a peptide-based drug as a highly selective chemokine antagonist.
Peptide Drugs Type
Different types of peptide therapeutics are available to treat various diseases, and their classification based on route of administration is as follows; oral and parenteral, parenteral drugs are further classified into intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous.
Oral Peptide Drugs:
Oral peptide drugs are most convenient and preferred drugs by the patients, as their mode of administration is through mouth, which allows quick, simple and non-invasive mode of taking the medication.
Form/ ingredients used:
Oral peptide drugs used for the treatment of various disease includes, Desmopressin DDAVP, Cyclosporin A Sandimmune/Neoral among others.
Peptide-Oral Drug Mode of Action:
Desmopressin acetate (DDAVP, 1-desamino-8-D-arginin-vasopressin) is a synthetic oligopeptide used for the treatment of enuresis nocturna and diabetes insipidus centralis in both children and adults.
It acts via binding to V2 receptors, on Basolateral membrane of the collecting duct in the kidneys which leads to insertion of aquaporin (AQP-2) water channels into the apical membrane, which increases water reabsorption, this reduces urine output, so useful for enuresis nocturna. Also stimulates release of von Willebrand factor and factor VIII from endothelial cell, which Reduces bleeding time so making it beneficial for mild haemophilia A.
Peptide Drugs Application:
Peptide drugs present several key advantages over small molecules, primarily characterized by heightened target specificity and potency, often demonstrated by EC50 values in the nanomolar range or lower. This increased specificity leads to fewer side effects, as peptide therapeutics are less likely to interact with unintended biological targets. The inherent diversity of side chains in peptides enables a broad spectrum of potential targets, enhancing their therapeutic versatility
Few current applications of therapeutic peptides in various diseases include the following:
- Therapeutic peptide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
T2DM has been successfully treated with peptide drugs, including GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and the best-known peptide drug, insulin.
- Therapeutic peptides in the treatment of cancer
Some of the modified peptides with good stability, for example, stable α-helical peptides as inhibitors of MDM2 and MDMX are used for the treatment of p53-dependent cancer.
Few US FDA approved peptide drugs are as follows:
| Drug | Disease | Mode of administration |
| Flotufolastat (Posluma) | Prostate cancer | Intravenously |
| Trofinetide (Daybue) | Rett syndrome | Orally |
| Rezafungin (Rezzayo) | Candidemia and invasive candidiasis | Intravenously |
One major alternative to peptide-based treatments is small-molecule drugs. These traditional pharmaceuticals have been the cornerstone of treatment for decades, particularly for chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and neurological conditions. Monoclonal antibodies and protein-based therapies, represent another significant alternative. It is used in the treatment of conditions like cancer, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases. Gene therapies are an emerging alternative, particularly for genetic disorders, and are gaining traction in areas like rare diseases and oncology.
Peptide Drugs Product Development Steps:
Some of the new product approvals by US FDA includes:
- October 2024: Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Inc. received an approval from FDA for Linzess (linaclotide) capsules as the first treatment specifically for functional constipation in pediatric patients aged 6 to 17 years. The recommended dosage for this age group is 72 mcg taken orally once daily. The approval is based on findings from a 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, which demonstrated the drug's efficacy in treating functional constipation in children, alongside supportive data from trials in adults with chronic idiopathic constipation.
- May 2022: The FDA approved Mounjaro (tirzepatide) injection from Eli Lilly and Company as the first and only GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist for treating adults with type 2 diabetes. This once-weekly injection is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control. In phase 3 SURPASS clinical trials, Mounjaro demonstrated superior A1C reductions compared to all comparators, and while it is not indicated for weight loss, it showed significant weight reductions in a key secondary endpoint. Mounjaro represents the first new class of diabetes medications introduced in nearly a decade and is expected to be available in the U.S. shortly.
- March 2022: The FDA granted approval to Novartis for Pluvicto (lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan), marking it as the first targeted radioligand therapy for adults with progressive, PSMA-positive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). This decision follows the successful results from the pivotal Phase III VISION trial, which demonstrated a significant reduction in the risk of death for patients receiving Pluvicto alongside standard care. Additionally, the FDA approved the complementary diagnostic agent Locametz, radiolabeled with gallium-68, to identify PSMA-positive lesions. Novartis aims to expand the application of Pluvicto in earlier treatment stages, with ongoing studies focused on earlier lines of therapy for metastatic prostate cancer.
The general overall procedure of peptide drug development and approval process follows these steps:
(1) Preclinical investigation- which will involve drug discovery and animal testing.
(2) Clinical investigation- This step will include different phases of testing on humans, step important to decide dosage, check for any adverse effects of the drug.
(3) Post-approval marketing surveillance this includes following regulatory guidelines even after drug approval and its sale in the market for ensuring its safety and efficacy all the time.
Other than these general steps there are some major regulatory steps, they are as follows:
Investigational New Drug Application: If preclinical studies show promising results, pharmaceutical company submits an investigational new drug (IND) application to FDA, detailing drugs potential and safety data.
New Drug Application and Biologics license applications: Upon successful completion of clinical trials, New Drug Application (NDA) pertain to traditional small molecule drugs, is submitted to FDA, providing comprehensive data on drugs safety and efficacy. This submission is the key step in getting the drug approved. LA is a request to approve the biological product for interstate commerce. It contains all the information of the development process and demonstrate the biological products safety, purity and potency, as well as it contains proposed packaging and labelling information of the drug. As per BPCI act of 2009, all biologics must be approved under BLA pathway and licensed under Section 351 of the Public Health Service (PHS) Act, in addition to being regulated by the FD&C Act.
Peptides Drugs Market Size Overview:
As per MRFR analysis, the Peptides Drugs Market Size was estimated at 40,993.68 (USD Million) in 2024. The Peptides Drugs Market Industry is expected to grow from 45,195.53 (USD Million) in 2025 to 1,25,552.42 (USD Million) till 2035, at a CAGR (growth rate) is expected to be around 10.76% during the forecast period (2025-2035). Growing awareness of peptide-based therapeutics, growing acquisition and agreement associated with peptide products and Increasing launch of platform to accelerate peptide drug discovery research are the key market drivers enhancing the growth of the market.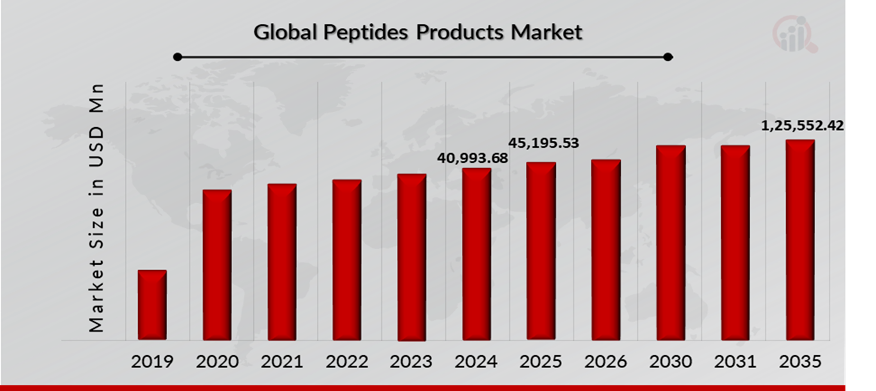
Source: The Secondary Research, Primary Research, MRFR Database and Analyst Review
Peptide Drugs Regulatory Landscape:
There are several key regulatory agencies oversee the approval and monitoring of oncology drugs to ensure their safety, efficacy, and quality.
| Regulatory agencies | Regulatory Ministry |
| Federal Food and Drug Administration | United States: Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) |
| The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency | United Kingdom: The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) under the Department of Health and Social Care (DHSC) |
| Central Drug Standard Control Organization | India: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare |
| South African Health Products Regulatory Authority (SAHPRA) | National Department of Health. |
| Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) | Japan: Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. |
| National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) | China: The Ministry of Health |
| Health Sciences Authority | Singapore: The Ministry of Health |
| European Medicine Agency | European union |
| Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency (Anvisa) | Ministry of Health, part of the Brazilian National Health System (SUS) |
Peptide Drugs Guidelines:
Eligibility: Peptide drugs are prescribed based on specific medical condition, eligibility depends on the type of disease patient is having, their age, available peptide drugs if are suitable for them or not, another overall health history of the patient. Peptide drugs are developed for the treatment of Diabetes Mellitus, Obesity, Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS), Human Growth Hormone(hGH) Deficiency, Hemophilia, Acromegaly, Hypoparathyroidism, Cancer, Neurological disorders, Cardiovascular Disorders, and Others, patient suffering from any of these health conditions may undertake suitable peptide drugs prescribes by the health professionals to overcome the disease.
Due to the complex synthesis process and stability requirements, establishment of targeted mechanisms can make these drugs costly, which may become accessibility limitation for some patients. Additionally, peptide drugs are often considered when conventional treatment options fail in the treatment in certain patients and diseases.
Dosage: Dosage of peptide drugs depends on the type of drug selected for the treatment, as peptide drugs are used to treat various diseases, it also depends on type of disease and age and other medical history of the patient.
For example, REZZAYO is a drug which is prescribed to the patients with age 18 or more who don’t have alternative option for the treatment of candidemia and invasive candidiasis. Recommended dosage of REZZAYO administration is once in a week by intravenous (IV) infusion, initial dose of 400 mg as a loading dose, then 200 mg dose once a weekly thereafter. The REZZAYO safety beyond 4 weeks doses has not been established.
Peptide Drugs Classification of the Product:
Peptide Drug Regulatory Process Overview, By Country:
According to the guidance issued by the centre for drug evaluation and research (CDER), of FDA the clinical pharmacology considerations for the peptides drugs, that industry should follow are as follows:
FDA’s Clinical pharmacological considerations has focused on considerations for assessing immunogenicity, characterising the impact of hepatic impairment, considerations for assessing drug interactions, charactering QT interval prolongation and labelling considerations for peptide drugs.
Considerations for assessing immunogenicity
- Immunogenicity risk assessment
Peptide drug products can show immunogenicity in the patients upon its administration.
Hence for preventing such issues and ensuring safety and efficacy of these drugs, certain immunogenicity assessments can be done, and this includes evaluation of factors which are product-specific (e.g., molecular size and structure), then process-specific factors (e.g. Proteins of host cells), subject-specific factors (e.g., state of disease), and factors related with design of study and use of product (e.g. Dosing regimen, administration route, and concomitant drugs).
- Clinical Immunogenicity Assessment
FDA recommends multiple assays for measuring responses of immunity of different domains. It also suggests developing assays for anti-drug antibody detection (ADA), for the peptide product having homology in sequence to endogenous protein or protein counterpart to measure the cross reactivity of ADAs in between the peptide drug product and the endogenous counterpart.
- Immunogenicity Clinical Impact Analysis
Designing clinical immunogenicity assessment for checking the impact of ADAs on peptide drugs products variables such as PK, PD, effectiveness and safety. This assessment should be done between subjects with ADA positive test and with ADA negative test, and also within subjects with before ADA positive and after ADA positive, The ones who are ADA positive, are further evaluated for effect of antibody titres, neutralizing antibody, PK, PD, efficacy, and safety assessment.
Impaired Health Impact Characterization
In rare cases hepatic impairment has impact on peptide clearances, they are primarily degraded by ubiquitous proteases. But some peptide characters can result into hepatic impairment, so certain factors should be considered in assessment which are as follows:
Peptide products showing hepatic metabolism substantial (>20%) have risk of increased plasma exposure, due to hepatic impairment.Peptides products from structural modifications; Cyclic peptides (e.g., cyclosporine) susceptible to metabolism by liver enzyme
If peptide products are eliminated with biliary excretion is >20%, elimination impact with increased plasma exposures as a result of hepatic impairment, even if hepatic metabolism is not significant.
Drug Interactions Assessment Considerations
- Pharmacokinetic Interactions
Peptide drugs generally don’t modulate CYP enzymes, drug transporters, but there are structural modifications in peptide drugs then they may modulate, these drugs should be assessed under in vitro conditions for determining if they have >20% binary and hepatic elimination, or active renal secretion >25%.
- Pharmacodynamic Interactions
Pharmacodynamic interactions can be exhibited by the peptide drugs with concomitant drugs, if pharmacological effect of one drug is altered by other, therefore it is encouraged for sponsors to have consultation with FDA for the pharmacodynamic drug interactions assessment.
QT interval prolongation characterisation
Natural peptides have no risk of direct ion channel interaction, but if mechanistic or clinical data has shown a given peptide drug possessing proarrhythmic potential, then QT studies may be warranted.
sponsors are suggested to give plan of QT assessment, and QTc prolongation risk which aligns with FDAs recommendatory guidelines, extent and timing of clinical QTc assessment will depend on overall risk or benefit profiles of peptide drug.
Labelling considerations
Labelling on drug products must contain certain important scientific information for the effective and safe use of these drugs which is as follows:
Labelling should be informative and accurate and not promotional or misleading, it must include information about PK and PD of peptide drug. The labelling of peptide drugs If the proteolytic and hydrolytic enzymes metabolize them primarily, it should be included under metabolism subheading below elimination heading in pharmacokinetics subsection of clinical pharmacology section.
Peptide Drugs Regulatory Updates and Amendment’s:
As peptide drugs are becoming increasingly important in therapeutics required for the treatment of various diseases. To facilitate evaluation of these drugs proposed generic equivalents. FDA is developing the scientific tools.
Existing guidelines didn’t focus on the quality of peptide drugs, and regulatory agencies are trying to cover up this gap, FDA has published 2 new general chapters in 2021 and 2023, including USP <1503> (Official date: 01-Aug-2021) and USP <1504> (Official date: 01-Dec-2023). The first one focuses on addressing specific considerations of quality for synthetic peptide drugs and the later focuses on providing recommendatory guidelines on minimum quality attributes stating products to be used for manufacturing of synthetic peptides.
In October 2023, a guidance draft was issued by EMA on development and manufacturing of synthetic peptides for public consultation to cover synthetic peptides with more than 4 amino acids(tetrapeptides) and below are considered as a small molecule
Peptide Drugs Regulatory Challenges:
- Peptide drugs face major issue of enzymatic degradation or instability issues which can affect their efficacy and can make them lose their therapeutic effect.
- They have major problem of immunogenicity, upon their entry in patients’ body they may trigger unwanted immune response which can in turn cause adverse effects in patients’ body.
- In case of oral drugs there is a problem of bioavailability, as drug when moving from GIT, gastrointestinal tract, can degrade or can have low permeability across membranes.
- Unwanted interaction of peptide drugs in the surrounding can become toxic to patients’ body or can go and bind off target site.
Possible Risk in development of Peptide Drugs:
- The growth of the global peptide market is significantly restrained by the side effects associated with peptide products. While peptides offer targeted therapeutic benefits, adverse reactions such as hormonal imbalance, fluid retention, increased hunger, discomfort from nausea, frequent headaches, joint discomfort, increased diabetes susceptibility, and potential for insulin resistance. raise concerns among both patients and healthcare providers. These side effects can lead to reduced patient adherence to treatment regimens and may discourage the prescription of peptide therapies, limiting their market potential.
- The need for rigorous safety assessments and regulatory approvals for new peptide formulations further complicates market entry, impeding innovation and expansion within the sector. As a result, the perception of risk associated with peptide products continues to challenge their widespread adoption and overall market growth.
Risk mitigation strategies for Peptide Drugs:
- Drug can be coated with protective layer (nanoparticle coating) to prevent its degradation on its route to target site.
- Enzyme inhibitors can be used which will block the activity of enzymes which can degrade it and drug can remain active for long time providing its therapeutic effect.
- To prevent off target delivery of peptide drugs nanoparticles can be used for showing therapeutic effect at disease target.
- To prevent immunogenicity, it is suggested to avoid immunogenic epitopes in the peptide drug product.
Peptide Drugs Competitive Landscape Dashboard:
Companies With Marketed Peptide Drugs Products
- Sanofi
- Novartis AG
- Pfizer Inc.
- Amgen Inc.
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Sun Pharmaceutical
- Industries Ltd
- Merck KGaA
- AstraZeneca
- Ironwood
- Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Takeda Pharmaceutical
- Company Limited
Regulatory Landscape - Table of Content
Table of contents will appear here once available.
Customer Stories

“This is really good guys. Excellent work on a tight deadline. I will continue to use you going forward and recommend you to others. Nice job”

“Thanks. It’s been a pleasure working with you, please use me as reference with any other Intel employees.”

“Thanks for sending the report it gives us a good global view of the Betaïne market.”

“Thank you, this will be very helpful for OQS.”

“We found the report very insightful! we found your research firm very helpful. I'm sending this email to secure our future business.”

“I am very pleased with how market segments have been defined in a relevant way for my purposes (such as "Portable Freezers & refrigerators" and "last-mile"). In general the report is well structured. Thanks very much for your efforts.”

“I have been reading the first document or the study, ,the Global HVAC and FP market report 2021 till 2026. Must say, good info! I have not gone in depth at all parts, but got a good indication of the data inside!”

“We got the report in time, we really thank you for your support in this process. I also thank to all of your team as they did a great job.”