
Regulatory Landscape - Overview
mHealth Regulatory Landscape: Product Overview
mHealth is an abbreviated version of mobile health technology, it basically mobile and wireless technology utilised in medical care, it involves medical and public health practice and make use of mobile devices, like mobile phones, patient monitoring devices, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and other wireless devices. It helps in surveillance of disease, treatment of various disease, epidemic outbreak tracking and chronic disease management.
mHealth Types
mHealth devices are broadly divided into following categories:
Remote monitoring apps: they help the healthcare practitioners to monitor patients’ health status even when they are at home, like monitoring blood glucose levels, oxygen level, heart rate, blood pressure, without visiting the patient.
Clinical and diagnostic apps: This app is involved in gathering, evaluating, and sharing data of patients, including the ability to access electronic health records (EHRs), review lab results, and even help in performing digital imaging. They have Built-in symptom identifiers helping the healthcare practitioners and patients to diagnose quickly any health issues or injuries. They are even useful for hassle-free patient scheduling.
Clinical reference apps: With these apps, there is no need of searching for references and guides. All the information required is provided at the fingertips. It provides digital access to E&M coding, ICD-9 and ICD-10, and other essential reference documents.
Healthy living apps: they are designed for helping to maintain and monitor the health every day for patients, mostly involved in monitoring health factors like heart rate, diet, exercise, and sleep. They are beneficial for the diabetes and heart patients.
Productivity apps: They increase the efficiency within the healthcare providers, designed for mobile charting, scheduling home healthcare, internal business communication, and remote dictation. The app provides all the necessary functions and even maintain the compliance Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) HIPAA.
mHealth Applications
Applications where mHealth is involved includes monitoring diabetes, monitoring rate of heartbeats through wrist watches, drug adherence ingestible sensors and apps providing health advice after mentioning the physical or psychological symptoms- telemedicine. Furthermore, there are step counting, calorie intake counting and personal fitness training technology apps available helping to maintain health every day.
Mhealth trends
In November 2023, AstraZeneca has launched Evinova, a new health-tech business aimed at accelerating innovation in the life sciences sector. Evinova will focus on digital health solutions, including remote patient monitoring and digital therapeutics, and has partnered with clinical research organizations like Parexel and Fortrea. The goal is to optimize clinical trial design and delivery, reducing development time and costs. Evinova's technologies have already been used successfully in over 40 countries and is available in 80 languages.
June 2024, Ryde Group Ltd has partnered with Mobile-health Network Solutions (MaNaDr) to enhance telehealth and quick commerce services. This collaboration aims to improve the well-being of Ryde's driver-partners and their families by providing affordable healthcare access through MaNaDr's 24/7 telemedicine platform. The partnership will benefits includes, access to members rate telemedicine consultations, joint marketing campaigns to increase brand awareness and provide convenient healthcare solutions.
mHealth Product Development Steps:
Centre for device and radiological health (CDRH) is responsible for the regulation of medical devices including mHealth software functions, office of product evaluation (OPEQ) conducts the review and evaluation of all the medical devices for ensuring its safety and efficacy under Food and drug administration (FDA).

Fig: overview of product development and approval process
mHealth Market Size Overview:
As per MRFR analysis, the mHealth Market Size was estimated at 60.43 (USD Billion) in 2022. The mHealth Market Industry is expected to grow from 66.18 (USD Billion) in 2023 to 150.0 (USD Billion) by 2032. The mHealth Market CAGR (growth rate) is expected to be around 9.52% during the forecast period (2024 - 2032).
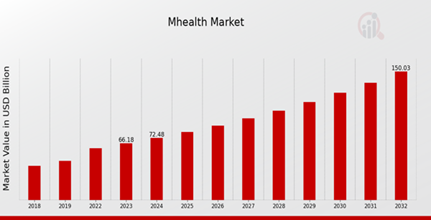
Source: Primary Research, Secondary Research, MRFR Database and Analyst Review
mHealth Regulatory Landscape:
There are several key regulatory agencies who oversee the approval and monitoring of mHealth to ensure their safety, efficacy, and quality.
| Regulatory agencies | Regulatory Ministry |
| Federal Food and Drug Administration | United States: Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) |
| The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency | United Kingdom: The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) under the Department of Health and Social Care (DHSC) |
| Central Drug Standard Control Organization | India: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare |
| South African Health Products Regulatory Authority (SAHPRA) | National Department of Health. |
| Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) | Japan: Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. |
| National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) | China: The Ministry of Health |
| Health Sciences Authority | Singapore: The Ministry of Health |
| European Medicine Agency | European union |
| Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency (Anvisa) | Ministry of Health, part of the Brazilian National Health System (SUS) |
mHealth Guidelines:
Eligibility for using mhealth medical service depends on type of health problem patient is facing, and local regulations. Generally, it is used for tracking the blood glucose levels by the diabetic patients, for remote monitoring of patient health by the healthcare providers in case the patients are not able to visit hospital regularly, for monitoring the heart rate for the cardiovascular disease patients, or those who want to take care of the general health conditions and wants to track their everyday steps, calorie intake, calories lost.
mHealth Classification of the Product:
mHealth egulatory Process Overview, By Country:
Mobile medical applications are often referred as software functions, which are software programs running on mobiles with intension to perform medical function, which range from aiding in disease diagnosis to monitoring patient health data. US FDA regulates these software functions for ensuring its quality, safety and efficacy.
Regulatory steps of these software functions are as follows
Determination of device classification
All medical devices are classified into three classes by FDA, including class I, class II, class III, first step is to assess whether software function meets the definition of medical device under 201(h) of federal food, drug, and cosmetic act (FD&CA).
Device is classified based on the risk it can pose to the patients
Class I – devices with low risk to patients and need to submit only general controls in approval process, and General Controls includes, registration, and Medical Device listing (21 CFR Part 807); Quality System (QS) regulation (21 CFR Part 820), Labeling Requirements (21 CFR Part 801), Medical Device Reporting (21 CFR Part 803), Premarket Notification (21 CFR Part 807), Reporting Corrections and Removals (21 CFR Part 806); and Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) requirements for clinical studies of investigational devices (21 CFR Part 812).
Class II- devices with moderate risk to patients and needs to submit General Controls (as described for Class I), Special Controls, and (for most Class II devices) Premarket Notification.
Class III- devices with high risk to the patients, usually include the devices which are life sustaining and need to submit General Controls (as described for Class I), and Premarket Approval (21 CFR Part 814). For getting grant of approval.
If a product is considered a medical device, the manufacturer must comply with certain FDA regulatory requirements. These requirements include
Establishment registrations and medical device listing
Manufacturers and distributors need to do establishment registration with the FDA, and electronic submission of all establishments is required, unless FDA has granted waiver, mostly they have to pay establishment registration fee to FDA. Devices must be listed with the FDA under appropriate category.
Submissions required
Premarket notification (510(K))- submit evidence indicating the device is substantially equivalent to legally marketed device. Mostly required for class II devices.
Premarket Approval (PMA) – mostly required for Class III devices, involves strict scientific and regulatory review for ensuring safety and effectiveness, it requires clinical data and detailed manufacturing information.
Medical device manufacturers should identify the current classification covering their device.
Manufacturers are required to prepare and submit to FDA an appropriate premarket
submission, as required for their device classification.
Investigational device exemption (IDE) for clinical studies: clinical studies should be conducted in by following IDE requirements (21 CFR 812) which ensure that are credible, accurate, and ethically collected clinical data. According to IDE it allows an investigational device use in clinical study, for collecting safety and effectiveness data needed to support marketing submission like Premarket Approval (PMA), Premarket Notification (510(k)), De Novo, Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE)) to FDA. If there is a significant risk with devices to be used in clinical study, it must be first approved by FDA and Institutional Review Board67 (IRB) before the study Starts, and devices with non-significant risk need approval of only IRB before start of the study.
Medical device manufacturers who intend to conduct research involving human subjects are
encouraged to engage with FDA through the Q-submission Program to receive feedback on
testing and development activities.
Quality system regulation – manufacturers need to ensure compliance with QS regulation, which gives framework to all manufacturers for developing products which will fulfil applicable requirements and specifications.
Labelling requirements- manufacturers of medical devices needs to comply with the requirements of labeling 21 CFR Part 801 for medical devices and 21 CFR Part 809 for in vitro diagnostic products.
Medical Device Reporting (MDR) (Adverse event reporting)
It must be submitted by manufacturer and importers to FDA if they become aware or find and issue with the approved and marketed device like contributed to death or injury to patient or malfunction.
According to guidelines for MDR, Medical device manufacturers must submit following to FDA:
- Report MDR events as per 21 CFR 803.10(c) and 803.50.
- Submit 5-day reports (21 CFR 803.53).
- Provide supplemental reports (21 CFR 803.56).
- Develop and maintain procedures to identify and evaluate MDR events (21 CFR 803.17).
- Investigate and determine the cause of each event (21 CFR 803.50(b)(3)).
- Keep complete files of all complaints about adverse events (21 CFR 803.18).
This ensures safety and efficacy of medical devices by monitoring and reporting the issues.
HIPPA - The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA)
the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in United States law, is involved in establishing national privacy standards for protecting patients’ medical records and health information, which is shared with healthcare professionals, medical offices, hospitals. HIPAA protect patient privacy, ensure data security, and regulate the use of patient’s sensitive health information.
mHealth News:
April 2021, The New platform called the Remote Diagnostics and Management Platform (RDMP) is launched by Mayo Clinic, for enhancing the analysis of data from mobile health (mHealth) devices. There is a integration of health data of patient with advanced artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to support clinical decision-making and provide continuous care. RDMP aims to deliver event-driven medicine. The platform will help clinicians to do fast and accurate diagnoses, allowing patients to take more care of their health.
mHealth Regulatory Challenges:
Compliance with Regulations: one of the biggest challenge for mHealth products is compliance with various regulations such as HIPAA in the US, and other local healthcare regulations, which makes process of ensuring compliance, complex and time-consuming.
Data Security and Privacy: Protecting patient data is important, manufacturers of mhealth products should develop security measures for protecting sensitive health information, which can be challenging, due to the increasing sophistication of cyber threats.
Approval Processes: FDA approval grant can be a lengthy and very strict process, which can delay the product launch in market for mHealth products.
Possible Risk in development of mHealth:
Technical Risks: Developing mHealth apps involves integrating various technologies such as IoT devices, cloud computing, and AI. Ensuring seamless integration and functionality can be risky and challenging.
User Adoption: Even if the app is technologically perfect, risk of users adoption of particular product is always present(both patients and healthcare providers), adoptability issues can be due to usability issues, lack of awareness, or resistance to change.
Financial Risks: Product development and manufacturing cost of mHealth products is very high and not necessary that the investment will give back expected results, if the app fails to gain traction in the market.
mHealth Competitive Landscape Dashboard:
Companies With Marketed mHealth Products
- Apple
- Fitbit
- UnitedHealth Group
- Qualcomm
- Philips
- HealthTap
- McKesson Corporation
- Johns Hopkins University
- Cerner Corporation
- IBM
- Samsung Electronics
- Medtronic
- Deloitte
Regulatory Landscape - Table of Content
Table of contents will appear here once available.
Customer Stories

“This is really good guys. Excellent work on a tight deadline. I will continue to use you going forward and recommend you to others. Nice job”

“Thanks. It’s been a pleasure working with you, please use me as reference with any other Intel employees.”

“Thanks for sending the report it gives us a good global view of the Betaïne market.”

“Thank you, this will be very helpful for OQS.”

“We found the report very insightful! we found your research firm very helpful. I'm sending this email to secure our future business.”

“I am very pleased with how market segments have been defined in a relevant way for my purposes (such as "Portable Freezers & refrigerators" and "last-mile"). In general the report is well structured. Thanks very much for your efforts.”

“I have been reading the first document or the study, ,the Global HVAC and FP market report 2021 till 2026. Must say, good info! I have not gone in depth at all parts, but got a good indication of the data inside!”

“We got the report in time, we really thank you for your support in this process. I also thank to all of your team as they did a great job.”